Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2006; 12(37): 5978-5986
Published online Oct 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i37.5978
Published online Oct 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i37.5978
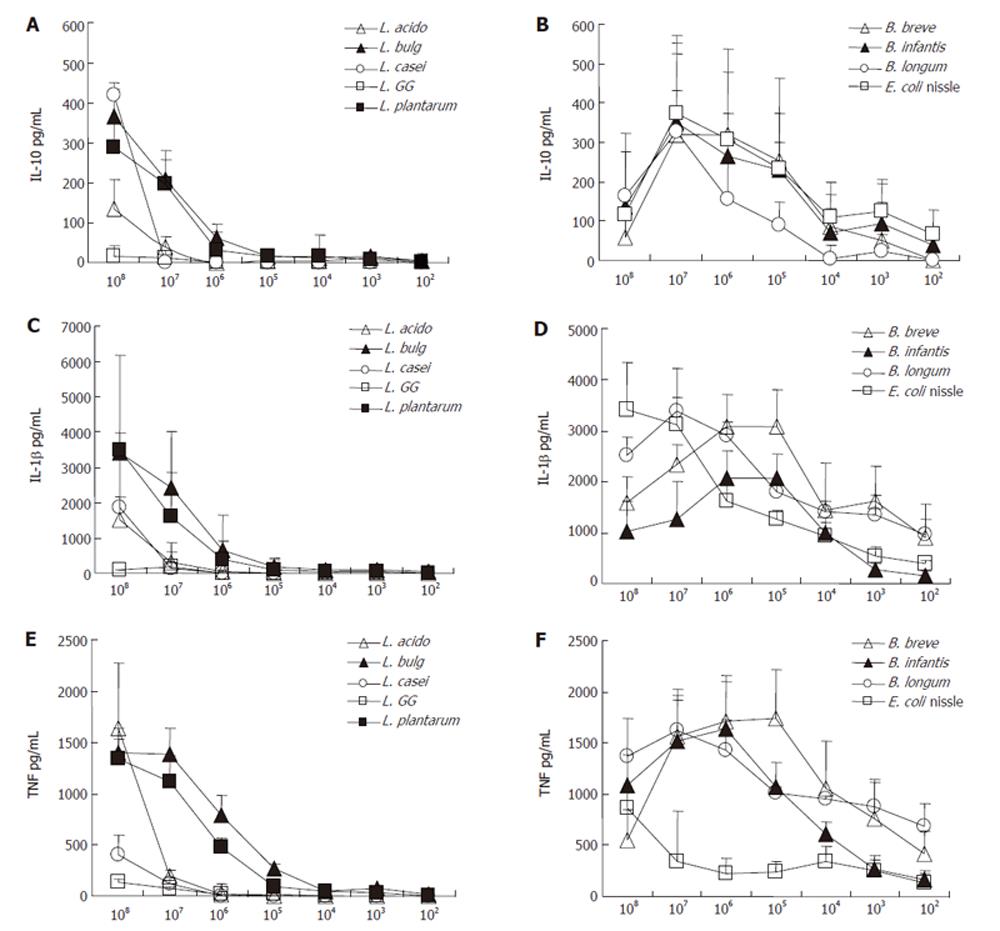
Figure 2 Cytokine concentration of supernatant after incubation of PBMNC with cell debris of bacteria in different concentrations.
A and B: supernatant concentration of IL-10 in pg/ml (mean ± SE); C and D: supernatant concentration of IL1β in pg/ml (mean ± SE); E and F: supernatant concentration of TNFα in pg/mL (mean ± SE). Lactobacilli are described on the left side and bifidobacteria are described on the right side.
- Citation: Helwig U, Lammers KM, Rizzello F, Brigidi P, Rohleder V, Caramelli E, Gionchetti P, Schrezenmeir J, Foelsch UR, Schreiber S, Campieri M. Lactobacilli, bifidobacteria and E. coli nissle induce pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(37): 5978-5986
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i37/5978.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i37.5978