Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2006; 12(30): 4836-4842
Published online Aug 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4836
Published online Aug 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4836
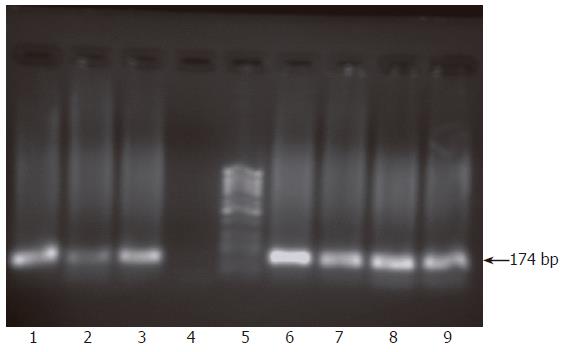
Figure 2 Monitoring of active viral replication at regular time intervals post infection of HepG2 cells.
RNA was extracted from infected cells and infectious supernatants and their passages at 1, 2 and 4 wk post infection and nested RT-PCR was carried out for detection of both viral strands. Results showed the presence of both viral strands in RNA extracted from cells 1 wk post infection (lanes 1, 2) but only the sense strand was detectable in the supernatant at this time point (lane 3) while the antisense strand was absent (lane 4). At 2 and 4 wk post infection, both viral strands were detectable in both cells and supernatant. Lanes 6-9 show the presence of both sense and antisense strands in both cells and supernatant at 4 wk post infection. Lane 5 shows molecular weight standard DNA marker (Ǿ-X-174/HaeIII; Q-BIOgene, Germany).
- Citation: El-Awady MK, Tabll AA, El-Abd YS, Bahgat MM, Shoeb HA, Youssef SS, Din NGBE, Redwan ERM, El-Demellawy M, Omran MH, El-Garf WT, Goueli SA. HepG2 cells support viral replication and gene expression of hepatitis C virus genotype 4 in vitro. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(30): 4836-4842
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i30/4836.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4836