Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2006; 12(27): 4281-4295
Published online Jul 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i27.4281
Published online Jul 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i27.4281
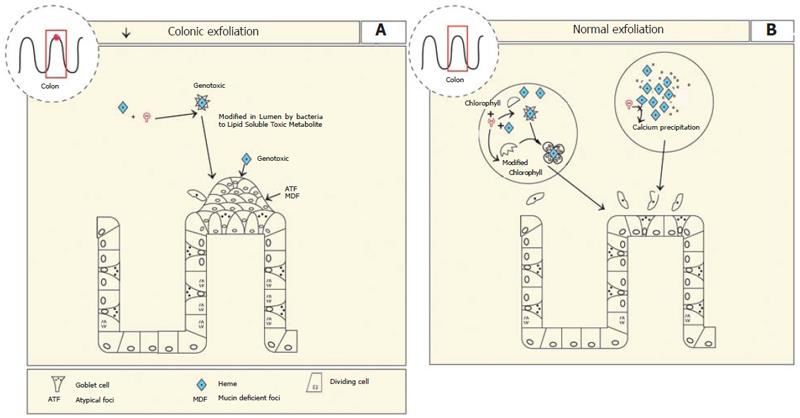
Figure 6 A: In the colon excess heme is metabolised into a lipid soluble heme metabolite possibly by commensal bacteria.
Heme itself is also genotoxic. This results in the formation of aberrant atypical foci, that are mucin deficient (ATF, MDF). Apoptosis is inhibited which could lead to increased survival of mutant cells; B: In the presence of calcium or chlorophyll heme precipitates into biological inactive compounds which inhibit the heme factor or binds the heme factor rendering it inert, respectively leading to normal colon growth.
- Citation: Oates PS, West AR. Heme in intestinal epithelial cell turnover, differentiation, detoxification, inflammation, carcinogenesis, absorption and motility. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(27): 4281-4295
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i27/4281.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i27.4281