Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2006; 12(26): 4232-4236
Published online Jul 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i26.4232
Published online Jul 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i26.4232
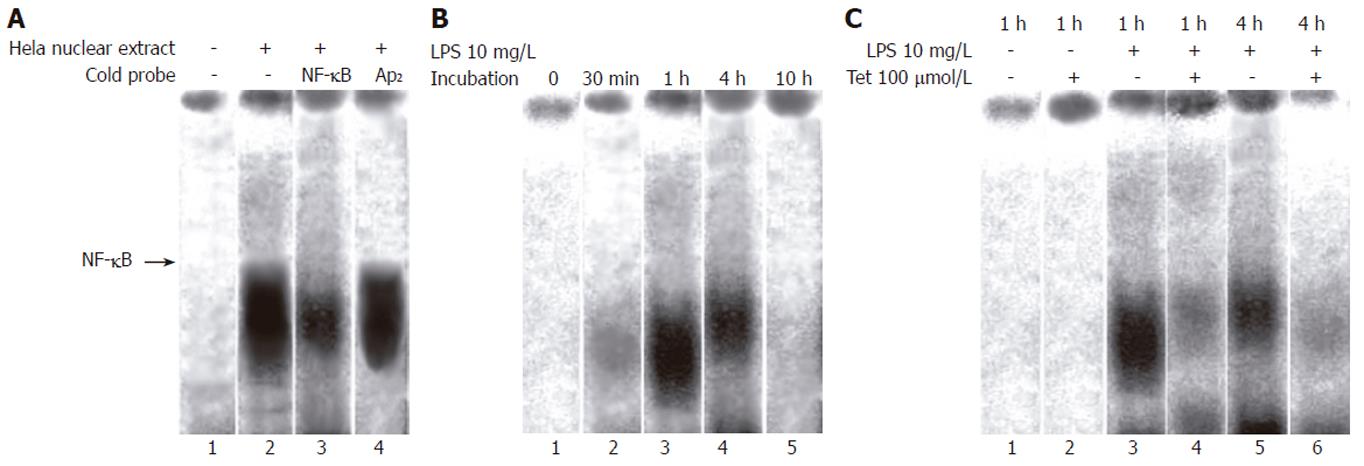
Figure 3 A: Effect of LPS on NF-κB activity in pancreatic acinar cell.
Lane 1: control; Lane 2: treated with LPS 10 mg/L for 1 h; Lane 3: treated with LPS 10 mg/L for 1 h + cold NF-κB probe; Lane 4: treated with LPS 10 mg/L for 1 h + labeled AP2 probe; B: The time course of LPS-induced NF-κB activity in pancreatic acinar cell. NF-κB activity in pancreatic acinar cell stimulated by LPS 10 mg/L for indicated periods of time. Lane 1: 0 min; Lane 2: 30 min; Lane 3: 1 h; Lane 4: 4 h; Lane 5: 10 h; C: Effect of Tet on LPS-induced NF-κB activity in pancreatic acinar cell. Lane 1: control; Lane 2: treated with Tet 100 μmol/L for 1 h; Lane 3: treated with LPS 10 mg/L for 1 h; Lane 4: treated with LPS 10 mg/L + Tet 100 μmol/L for 1 h; Lane 5: treated with LPS 10 mg/L for 4 h; Lane 6: treated with LPS 10 mg/L + Tet 100 μmol/L for 4 h.
- Citation: Zhang H, Li YY, Wu XZ. Effect of Tetrandrine on LPS-induced NF-κB activation in isolated pancreatic acinar cells of rat. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(26): 4232-4236
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i26/4232.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i26.4232