Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2006; 12(23): 3729-3735
Published online Jun 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i23.3729
Published online Jun 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i23.3729
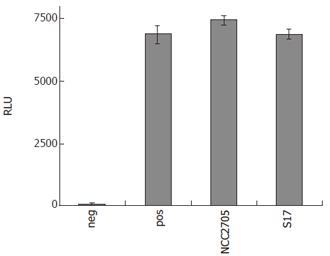
Figure 4 NF-κB-driven SEAP activity in the supernatants of HT-29 clone 34 cells pre-incubated with different bifidobacteria and subsequent stimulation with TNF-α (10 μg/L) for 16 h in the presence of 50 mL/L HM.
Cells treated with medium only served as negative control (neg) and positive controls (pos) were cells challenged with TNF-α + HM without bacterial pre-treatment. Results are given as RLU and are means ± SD of triplicate measurements of a representative of two independent experiments.
- Citation: Riedel CU, Foata F, Philippe D, Adolfsson O, Eikmanns BJ, Blum S. Anti-inflammatory effects of bifidobacteria by inhibition of LPS-induced NF-κB activation. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(23): 3729-3735
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i23/3729.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i23.3729