Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2006; 12(20): 3265-3270
Published online May 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i20.3265
Published online May 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i20.3265
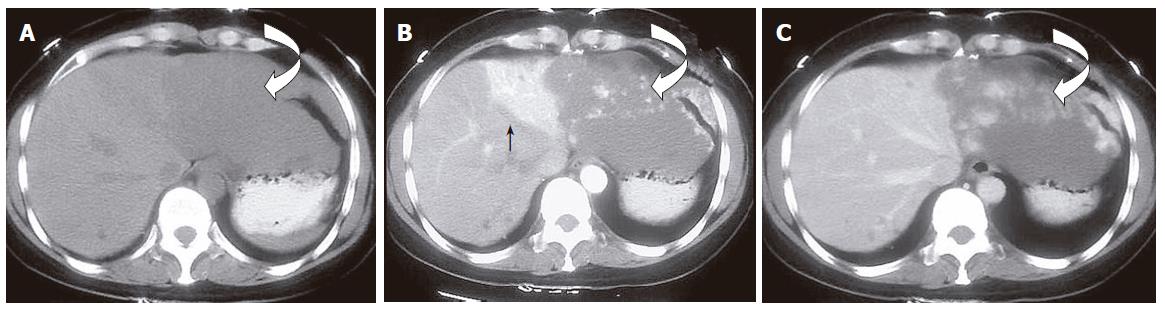
Figure 1 HPD in a 48-year-old woman with cavernous hemangioma.
A: Pre- contrast administration transverse CT scan shows a large well-defined hypo-attenuating lesion located in segment II(curved open arrow); B: HAP CT scan shows a nodular enhanced hemangioma (curved open arrow) and wedge-shaped segmental homogeneous hyperattenuating areas (solid arrow) adjacent to the tumor; C: PVP CT scan shows the still nodular enhanced hemangioma (curved) and the peripheral area resumed isoattenuating.
- Citation: Tian JL, Zhang JS. Hepatic perfusion disorders: Etiopathogenesis and related diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(20): 3265-3270
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i20/3265.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i20.3265