Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2006; 12(2): 214-221
Published online Jan 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i2.214
Published online Jan 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i2.214
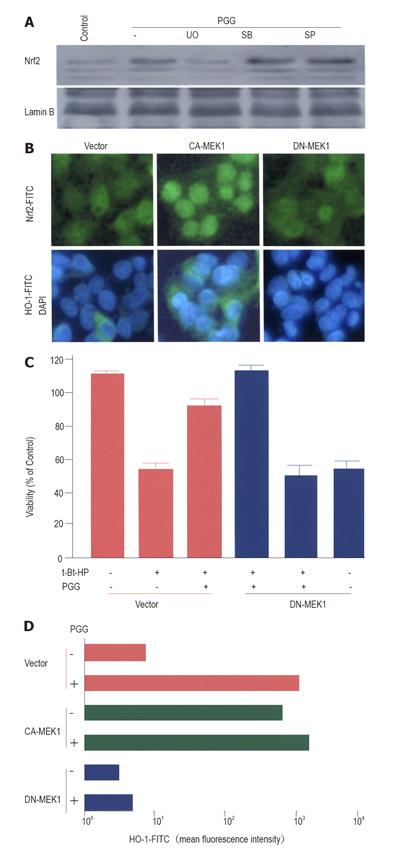
Figure 6 Roles of PGG-induced ERK activation in Nrf2 nuclear translocation and t-Bt-HP-induced toxicity in HepG2 cells.
A: Cells were incubated with 20 µmol/L PGG for 2 h in the presence or absence of 10 µmol/L U0123 (UO), 20 µmol/L SB203580 (SB), or 20 µmol/L SP600125 (SP), and nuclear extracts were harvested, following Western blotting analysis with Nrf2 antibody; B: Cells were transiently transfected with control vector (Vector), CA-MEK1 gene, or DN-MEK1 gene, stained with Nrf2 antibody (upper) or HO-1 antibody and DAPI (lower), and visualized using a fluorescent microscope; C: Cells transfected with control vector or DN-MEK1 gene were pre-incubated with 20 µmol/L PGG for 12 h, and exposed to 100 µmol/L t-Bt-HP for 4 h. Data are expressed as mean ± SE of five independent experiments; D: Cells transfected with vector or each gene were incubated for 12 h in the absence or presence of 20 µmol/L PGG. HO-1 expression was determined by a flow cytometry.
- Citation: Pae HO, Oh GS, Jeong SO, Jeong GS, Lee BS, Choi BM, Lee HS, Chung HT. 1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose up-regulates heme oxygenase-1 expression by stimulating Nrf2 nuclear translocation in an extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent manner in HepG2 cells. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(2): 214-221
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i2/214.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i2.214