Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2006; 12(19): 3123-3125
Published online May 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i19.3123
Published online May 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i19.3123
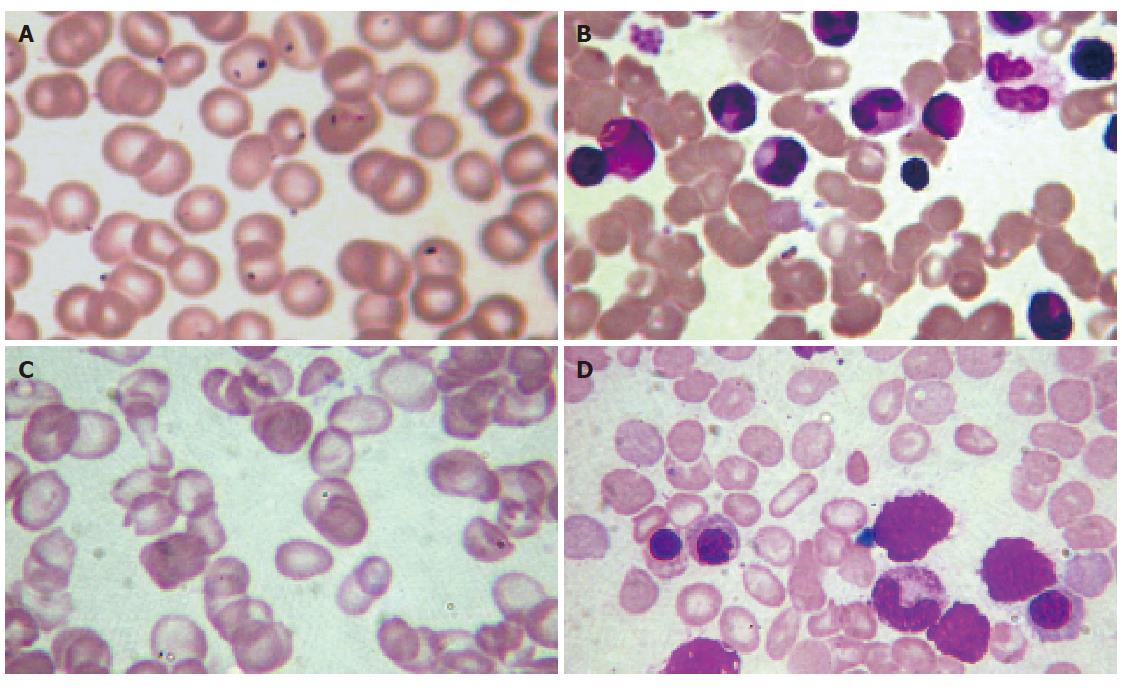
Figure 1 Peripheral smear and bone marrow aspirate.
A and B: Peripheral smear and bone marrow aspirate of a healthy volunteer, respectively (400×, Giemsa); C: Peripheral smear of the propositus, showing irregular erythrocytes in shape and size with mild macrocytosis and target-, rod-, tear-drop cells; D: Bone marrow aspirate of the propositus which revealed a erythroid hyperplasia and some target-, rod-, tear-drop erythrocytes.
- Citation: Wang CL, Liu XW, Lu FG, Wu XP, Ouyang CH, Yang DY. Primary shunt hyperbilirubinaemia in a large four-generation family confirming autosomal dominant genetic disorder. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(19): 3123-3125
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i19/3123.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i19.3123