Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2006; 12(19): 2969-2978
Published online May 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i19.2969
Published online May 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i19.2969
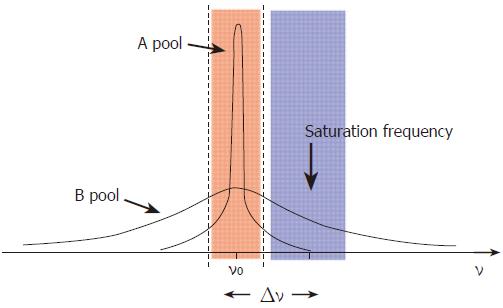
Figure 2 Model demonstrating the concepts underlying the phenomenon of magnetization transfer.
The free pool of protons (A) resonates at the Larmor frequency (ν0) and has a narrow spectral line. It is excited by an RF pulse which covers the frequencies shown in pink. The “bound” pool of protons (B) has a broad spectral line and can be excited and saturated by the application of RF irradiation at a frequency offset by Δν, shown in blue, without significantly affecting pool A.
- Citation: Grover VB, Dresner MA, Forton DM, Counsell S, Larkman DJ, Patel N, Thomas HC, Taylor-Robinson SD. Current and future applications of magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy of the brain in hepatic encephalopathy. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(19): 2969-2978
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i19/2969.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i19.2969