Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2006; 12(18): 2806-2817
Published online May 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i18.2806
Published online May 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i18.2806
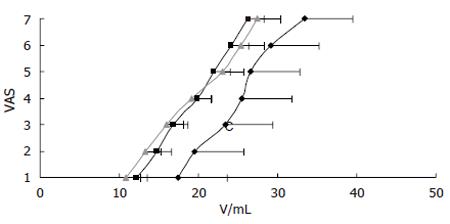
Figure 5 Stimulus-response function (mean ± SEM) to mechanical stimulation in patients with non-erosive gastro-esophageal reflux disease (NERD).
The controls (■, n = 15) and patients with a normal 24-h pH-profile (▲, n = 7) had similar response to the mechanical stimulation, whereas patients with pathological pH-profile (◊, n = 6) showed hypoalgesia to the stimulations. The x-axis shows the volume of the balloon in the distal esophagus and the y-axis denotes the pain response on a visual analogue scale (VAS) with 5 as the pain threshold.
- Citation: Drewes AM, Arendt-Nielsen L, Funch-Jensen P, Gregersen H. Experimental human pain models in gastro-esophageal reflux disease and unexplained chest pain. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(18): 2806-2817
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i18/2806.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i18.2806