Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2006; 12(16): 2477-2486
Published online Apr 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i16.2477
Published online Apr 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i16.2477
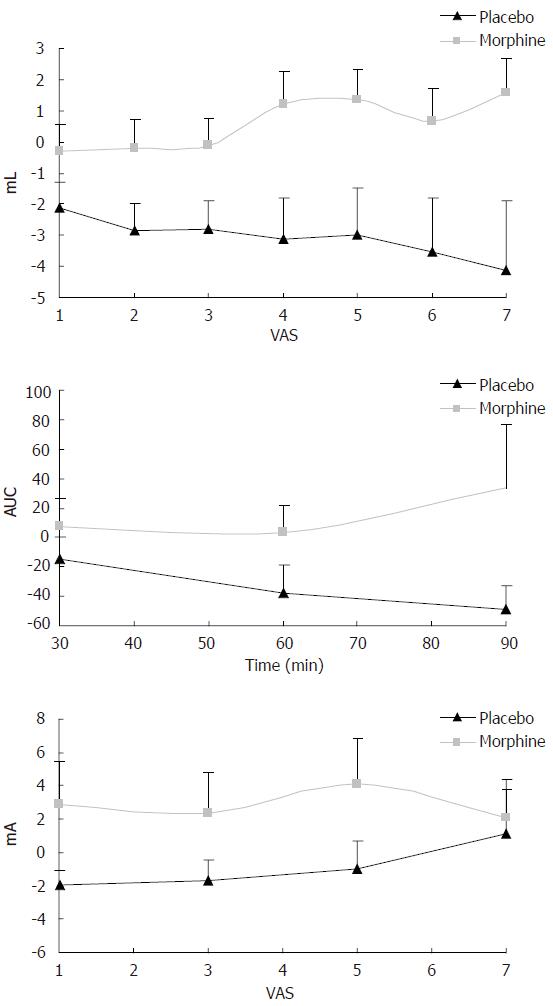
Figure 7 Change in sensory rating compared with baseline recordings for oral morphine and placebo using multimodal stimulation of the esophagus.
Top picture: Morphine attenuates mechanically evoked pain better than placebo 60 min after drug intake (P < 0.01). VAS on the X-axis denotes the sensory rating at a visual analogue scale with 5 as the pain threshold. ML at the Y-axis denotes the bag volume. Middle picture: Morphine attenuates heat pain better than placebo (P < 0.05). Here the X-axis illustrates time after drug intake (min) and AUC on the Y-axis denotes the area under the temperature curve used as a proxy for the thermal energy. Bottom picture: Morphine also worked better than placebo (P < 0.05) on electrical stimulation 60 min after drug intake.
- Citation: Drewes AM, Gregersen H. Multimodal pain stimulation of the gastrointestinal tract. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(16): 2477-2486
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i16/2477.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i16.2477