Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2006; 12(14): 2168-2173
Published online Apr 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i14.2168
Published online Apr 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i14.2168
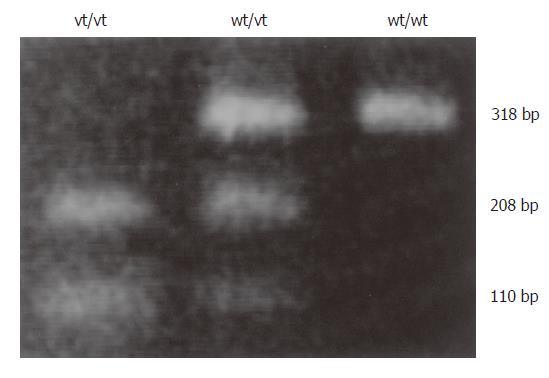
Figure 2 PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis of genetic polymorphism of the -160 site of the E-cad promoter.
The C/A polymorphism was differentiated by BstEII digestion of PCR products homozygous for the wild-type (high-activity) allele (wt/wt, CC gentoype), heterozygous for the variant (low-activity) allele (wt/vt, CA genotype), and homozygous for the low-activity allele (vt/vt, AA genotype)
- Citation: Liu YC, Shen CY, Wu HS, Hsieh TY, Chan DC, Chen CJ, Yu JC, Yu CP, Harn HJ, Chen PJ, Hsieh CB, Chen TW, Hsu HM. Mechanisms inactivating the gene for E-cadherin in sporadic gastric carcinomas. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(14): 2168-2173
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i14/2168.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i14.2168