Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2006; 12(11): 1657-1670
Published online Mar 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i11.1657
Published online Mar 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i11.1657
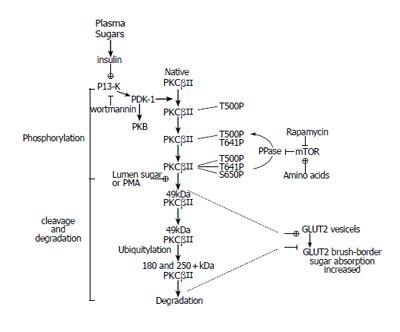
Figure 4 Potential signaling pathways for the regulation of GLUT2-mediated sugar absorption by insulin and amino acids through the control of PKC βII activity.
(from Helliwell et al, 2003). Abbreviations: PMA= phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, PDK-1=protein-dependent kinase-1, PI3K=phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase, PKB=protein kinase B, mTOR=mammalian target of rapamycin, PKCβII=protein kinase C βII.
- Citation: Drozdowski LA, Thomson AB. Intestinal sugar transport. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(11): 1657-1670
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i11/1657.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i11.1657