Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2006; 12(10): 1569-1576
Published online Mar 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i10.1569
Published online Mar 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i10.1569
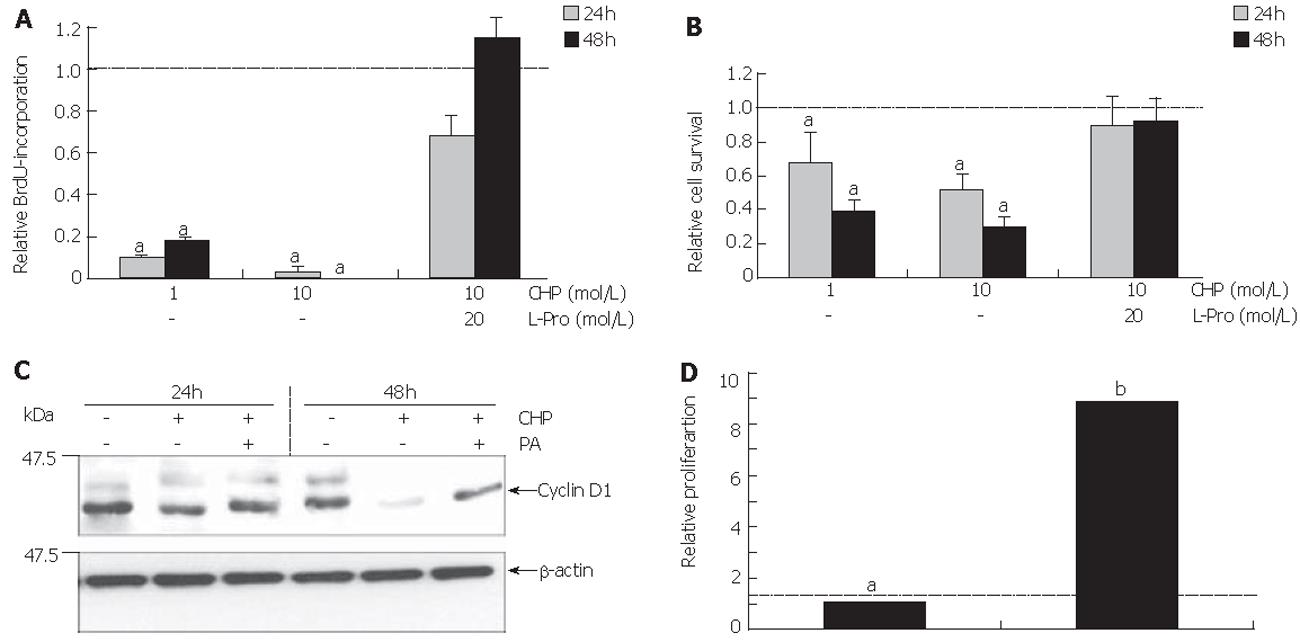
Figure 2 Inhibition of cell proliferation and survival by CHP.
A: After the addition of BrdU, cells were cultured for further 20 h, followed by quantification of BrdU incorporation; B: Four hours after the addition of CellTiter AQueous solution, conversation of the MTT salt was measured. CHP-caused decrease of proliferation (A) and metabolically active cells (B) was prevented by the addition of L-proline. Results are expressed as mean±SE (n = 6, aP≤ 0.05). C: Immunoblotting of total cell extracts from DSL6A cells using an anti-cyclin D1 antibody. Results are representative for three independent experiments. D: DSL6A cells were treated with 10 mmol/l CHP for 24 h before culture medium was (a) replaced by DMEM without CHP or (b) 20 mmol/L L-proline was added to the CHP-containing medium.
- Citation: Mueller C, Emmrich J, Jaster R, Braun D, Liebe S, Sparmann G. Cis-hydroxyproline-induced inhibition of pancreatic cancer cell growth is mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(10): 1569-1576
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i10/1569.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i10.1569