Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2006; 12(10): 1536-1544
Published online Mar 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i10.1536
Published online Mar 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i10.1536
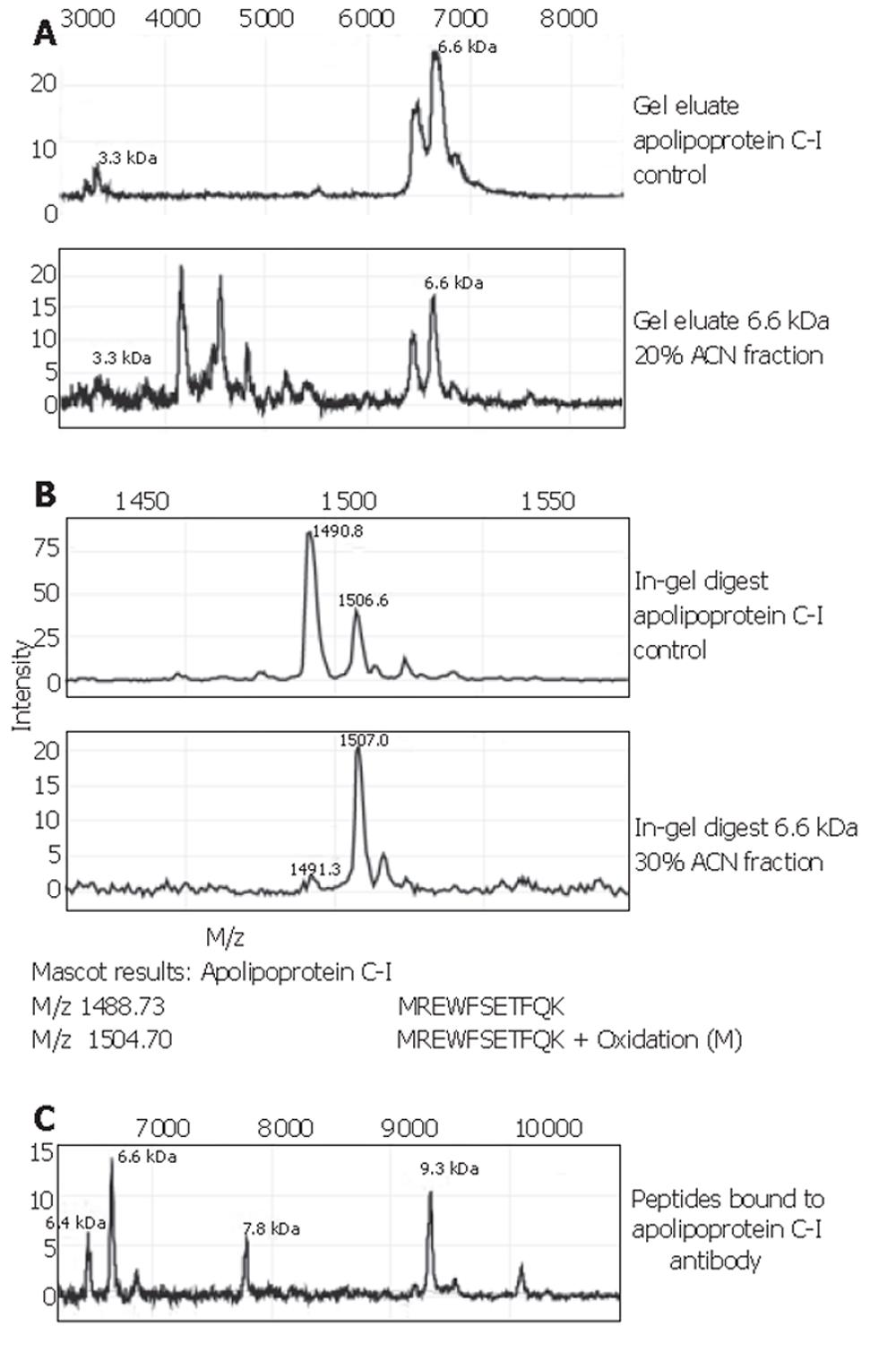
Figure 4 Identification of apolipoprotein C-I.
A: Parts of the MS spectra of the gel eluates of an apolipoprotein C-I control and the 6.6×103-Da protein isolated from HC serum run on the same gel. B: Parts of the MS spectra of the in-gel digests of an apolipoprotein C-I control and the 6.6×103-Da protein isolated from HC serum and the results of sequencing of these two peptides with tandem MS. C: Part of the MS spectrum of the eluate from the apolipoprotein C-I antibody. Apart from the expected peaks at 9.3×103, apolipoprotein C-I precursor, and 6.6×103, a 6.4×103-Da peak is seen, which is a known fragment of apolipoprotein C-I missing two N-terminal amino acids. The mass at 7.8×103 is unknown and does not correspond to any of the apolipoproteins with which antibody cross-reactivity can occur. It is possibly an intermediate splice form of the precursor protein.
- Citation: Engwegen JY, Helgason HH, Cats A, Harris N, Bonfrer JM, Schellens JH, Beijnen JH. Identification of serum proteins discriminating colorectal cancer patients and healthy controls using surface-enhanced laser desorption ionisation-time of flight mass spectrometry. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(10): 1536-1544
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i10/1536.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i10.1536