Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2005; 11(8): 1149-1154
Published online Feb 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i8.1149
Published online Feb 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i8.1149
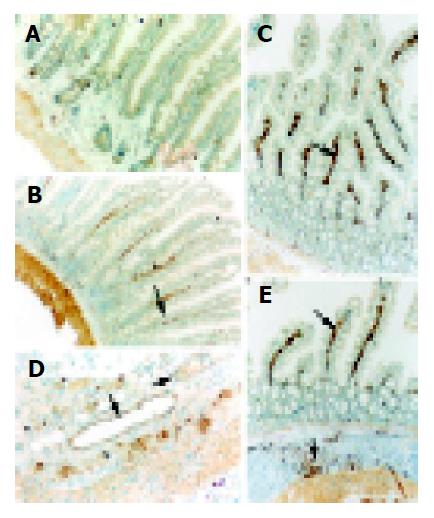
Figure 4 ICAM-1 immunohistochemical staining of jejunal tissue, indicated by the arrows.
A: almost undetectable ICAM-1 expression in the villi from control rats; B: moderate ICAM-1 immunoreactivity in the villous interstitium at 24 h postinjury, with the villi well defined; C: strong ICAM-1 immunoreactivity in the villous interstitium at 72 h postinjury, with the villi disarranged and the ICAM-1 positive endothelial cells shown as nigger-brown granules; D: marked ICAM-1 immunohistochemical staining of microvessels in the intestinal lamina propria at 72 h postinjury; E: high ICAM-1 immunoreactivity in the villous interstitium at 7 d postinjury, with the villi atrophic and sparse.
- Citation: Hang CH, Shi JX, Li JS, Li WQ, Yin HX. Up-regulation of intestinal nuclear factor kappa B and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 following traumatic brain injury in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(8): 1149-1154
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i8/1149.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i8.1149