Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2005; 11(8): 1149-1154
Published online Feb 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i8.1149
Published online Feb 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i8.1149
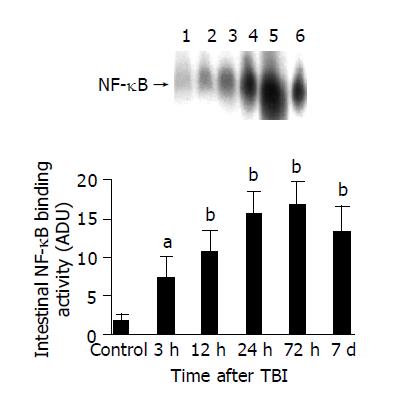
Figure 1 Jejunal NF-κB binding activity following TBI.
As compared with control group, NF-κB binding activity in the jejunal tissue following TBI significantly increased at 3 h after TBI, being highest at 72 h postinjury, and remained elevated by 7 d postinjury. Upper: EMSA autoradiogram. Lane 1, control; lane 2, 3 h postinjury; lane 3, 12 h postinjury; lane 4, 24 h postinjury; lane 5, 72 h postinjury; lane 6, 7 d postinjury. Lower: bar graph showing the mean band intensity of EMSA autoradiograph in the jejunal tissue of control, 3, 12, 24, 72 h and 7 d postinjury. aP<0.05, bP<0.01. mean±SD of six animals in each group.
- Citation: Hang CH, Shi JX, Li JS, Li WQ, Yin HX. Up-regulation of intestinal nuclear factor kappa B and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 following traumatic brain injury in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(8): 1149-1154
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i8/1149.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i8.1149