Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2005; 11(44): 6910-6919
Published online Nov 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i44.6910
Published online Nov 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i44.6910
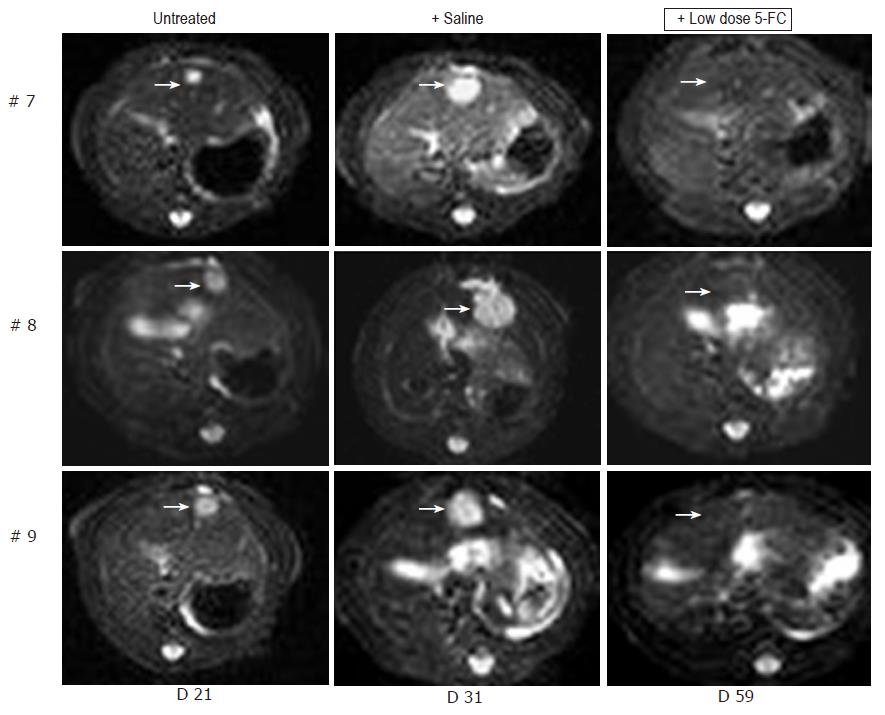
Figure 5 MRI detection of tumor growth of orthotopically implanted MH SuperCD hepatomas treated under a low-dose 5-FC regimen.
Animals #7, #8, #9 (column 1: tumor size at d 21), which first had been treated with saline only for over a 7-d period and thereafter, uniformly exhibiting a substantial tumor growth (column 2: tumor size at d 31), were then treated by a low-dose 5-FC regimen [twice weekly ip injections of 5-FC (283 mg/kg body weight)] over a 28-d period until d 59. Analysis of subsequent MRI sections did not reveal any MH SuperCD tumors (column 3, d 59: +low dose 5-FC); T2 weighed images are depicted; arrows in column 3 point out to places of former tumor localizations before the onset of 5-FC treatment.
- Citation: Graepler F, Lemken ML, Wybranietz WA, Schmidt U, Smirnow I, Groß CD, Spiegel M, Schenk A, Graf H, Lauer UA, Vonthein R, Gregor M, Armeanu S, Bitzer M, Lauer UM. Bifunctional chimeric SuperCD suicide gene -YCD: YUPRT fusion is highly effective in a rat hepatoma model. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(44): 6910-6919
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i44/6910.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i44.6910