Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2005; 11(44): 6910-6919
Published online Nov 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i44.6910
Published online Nov 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i44.6910
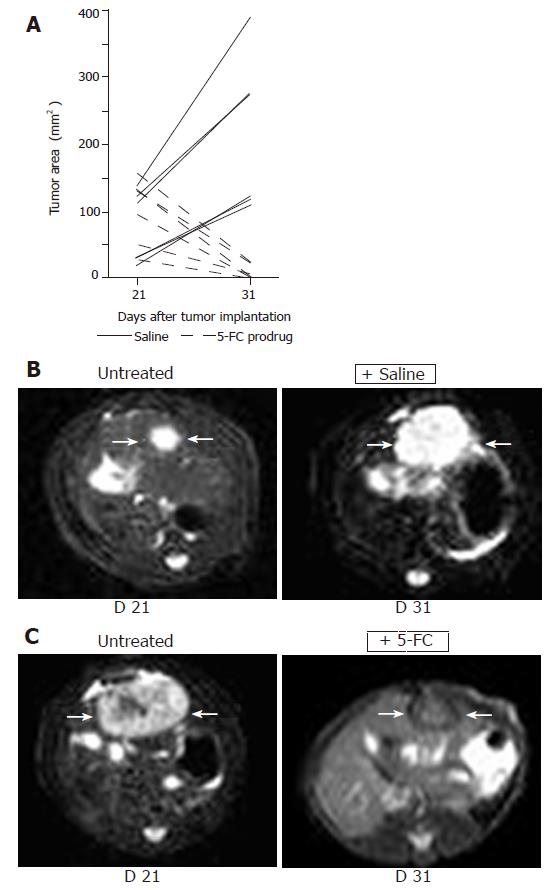
Figure 4 Non-invasive MRI detection of tumor growth of orthotopically implanted MH SuperCD hepatomas (saline vs 5-FC prodrug treatment).
Animals with MRI detectable liver tumors in T2 weighed images were randomized into two groups (6 rats/group) and treated twice daily with ip injections of saline or 5-FC (283 mg/kg body weight) over a 10-d period. Panel A: Maximum tumor areas (mm2) at d 21 and d 31; solid lines: tumor growth of control animals (saline-treated); broken lines: tumor regression of serum animals (5-FC-treated). Panel B: Representative MRI tumor images of the saline-treated control animal exhibiting the smallest tumor area at d 21 (left); and a dramatic tumor growth was observed at d 31 (right). Panel C: Representative MRI tumor images of the serum animal (treated with 5-FC) exhibiting the largest tumor area at d 21 (left); and a dramatic tumor regression was measured at d 31 (right).
- Citation: Graepler F, Lemken ML, Wybranietz WA, Schmidt U, Smirnow I, Groß CD, Spiegel M, Schenk A, Graf H, Lauer UA, Vonthein R, Gregor M, Armeanu S, Bitzer M, Lauer UM. Bifunctional chimeric SuperCD suicide gene -YCD: YUPRT fusion is highly effective in a rat hepatoma model. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(44): 6910-6919
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i44/6910.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i44.6910