Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2005; 11(41): 6495-6502
Published online Nov 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i41.6495
Published online Nov 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i41.6495
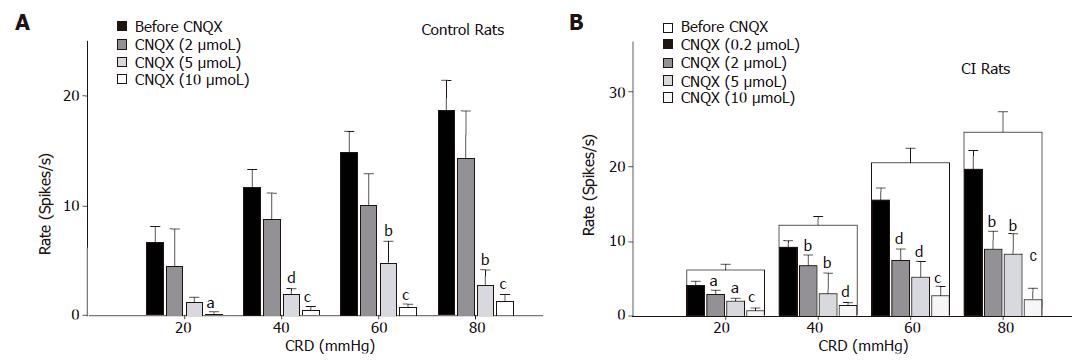
Figure 5 Effect of spinal CNQX on average responses of LS neurons to CRD.
Bar graphs illustrate the responses of LS neurons to graded CRD (20-80 mmHg) recorded in control rats (A; left panel) or CI rats (B; right panel) before and after spinal administration of CNQX. A: In control rats, CNQX (5 µmoL) significantly attenuated the responses to CRD in the 40-80 mmHg range and CNQX (10 µmoL) significantly attenuated the response to all intensities of CRD; B: In CI rats, CNQX (2-10 µmoL) significantly decreased the response to all intensities of CRD in a dose-dependent manner. aP<0.05, bP<0.01, dP<0.001 vs before CNQX application at that distention pressure in each group; cP <0.05 vs 2 µmoL CNQX.
- Citation: Lin C, Al-Chaer ED. Differential effects of glutamate receptor antagonists on dorsal horn neurons responding to colorectal distension in a neonatal colon irritation rat model. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(41): 6495-6502
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i41/6495.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i41.6495