Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2005; 11(39): 6134-6143
Published online Oct 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i39.6134
Published online Oct 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i39.6134
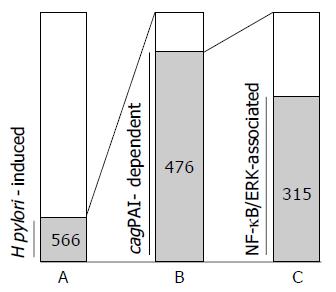
Figure 4 Characterization of the upregulated genes co-cultured with H pylori for 3 h (n = 566).
A: The bar represents the number of 566 upregulated genes among 3 228 analyzed genes (566 genes). B: The genes induced by cagPAI-positive H pylori infection among the 566-H pylori-induced genes (476 genes). C: The contribution of NF-kB or ERK signaling pathway among thecagPAI-dependent gene expression. Among the 476-cagPAI-dependent genes, 66% (315 genes) were also involved in the NF-kB- and/or ERK-signaling activation, whereas 34% (161 genes) of 476 genes were dependent on cagPAI but not involved in either NF-kB or ERK signaling activation.
-
Citation: Shibata W, Hirata Y, Yoshida H, Otsuka M, Hoshida Y, Ogura K, Maeda S, Ohmae T, Yanai A, Mitsuno Y, Seki N, Kawabe T, Omata M. NF-kB and ERK-signaling pathways contribute to the gene expression induced by
cag PAI-positive-Helicobacter pylori infection. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(39): 6134-6143 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i39/6134.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i39.6134