Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2005; 11(39): 6134-6143
Published online Oct 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i39.6134
Published online Oct 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i39.6134
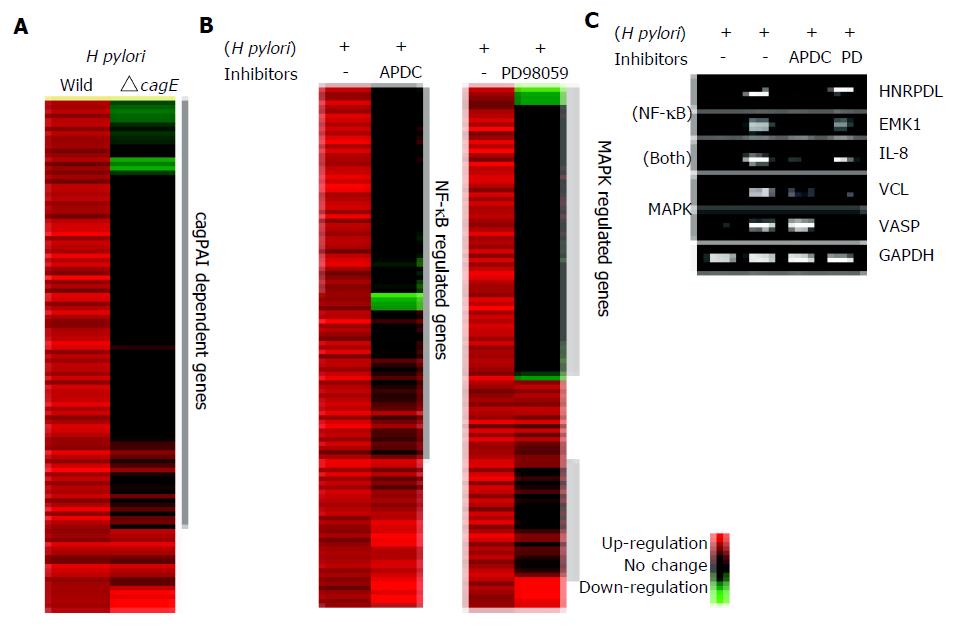
Figure 2 A: The contribution of the cagPAI-coded type IV secretion system to the gene expression profile in AGS cells.
Hierarchical clustering of genes induced by H pylori with or without a functional type IV secretion system (wild type or cagE mutant, respectively). Left lane; gene expression profile of AGS cells co-cultured with wild-type H pylori relative to control. Right lane; gene expression profile of AGS cells co-cultured with the isogenic mutant cagE. Only the 566 significantly upregulated genes at 3 h are shown. About 84% of the genes were induced only by the wild-type H pylori infection. These genes were supposed to be induced by the presence of cagPAI-coded type IV secretion system. B: The contribution of NF-kB or ERK pathways to the gene expression profile. Inhibitors specific for NF-kB or ERK were added to AGS cells co-cultured with H pylori. The gene expression profiles in the presence or absence of the inhibitors were compared. C: The changes in the expression of some representative genes were confirmed by RT-PCR. All genes were induced by wild-type H pylori infection, and suppressed by the incubation with inhibitors of specific signal pathways.
-
Citation: Shibata W, Hirata Y, Yoshida H, Otsuka M, Hoshida Y, Ogura K, Maeda S, Ohmae T, Yanai A, Mitsuno Y, Seki N, Kawabe T, Omata M. NF-kB and ERK-signaling pathways contribute to the gene expression induced by
cag PAI-positive-Helicobacter pylori infection. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(39): 6134-6143 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i39/6134.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i39.6134