Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2005; 11(37): 5816-5820
Published online Oct 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i37.5816
Published online Oct 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i37.5816
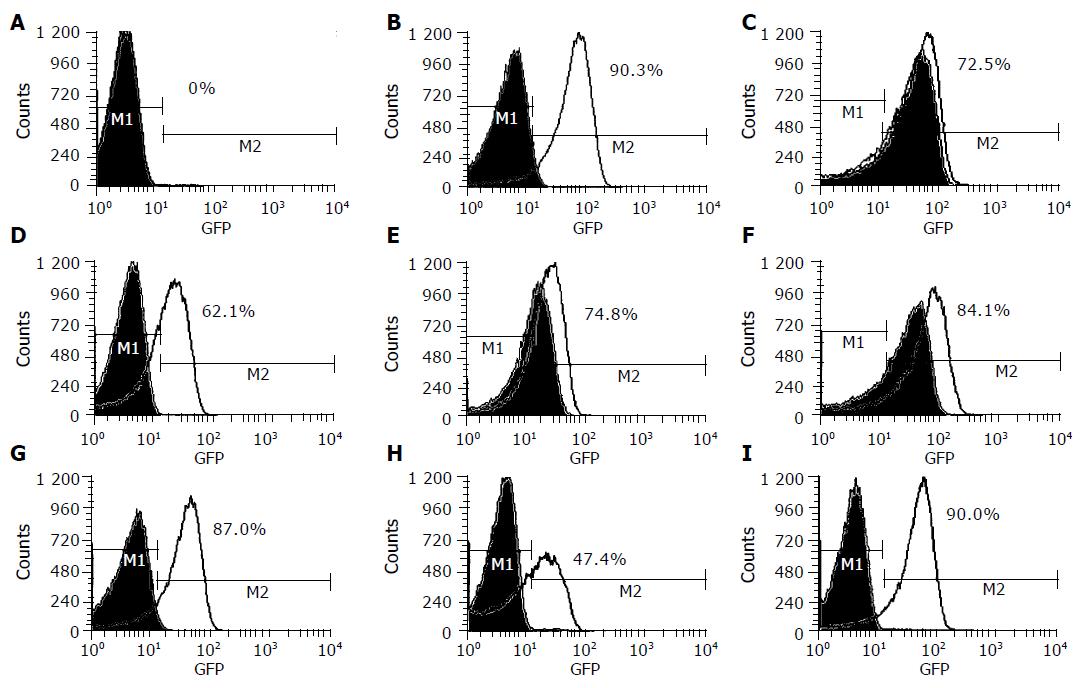
Figure 2 Fluorescence of fyuA-gfp in E.
coli grown on LB media (green curve) and LBD media (black curve). A: WA-CS irp1::KN(pCJG3.3N), CFT073(HPI+), HB101(HPI–) and EAEC 47/37(HPI–); B: WA(HPI+); C: EAEC 66(HPI+); D: EAEC SS23(HPI+); E: EAEC B86-2(HPI+); F: EAEC E1073(HPI+); G: EAEC 52/46(HPI+); H: EAEC 17-2 (HPI+); I: EAEC O42 (HPI+); M1: specified range of background of fluorescence signal; M2: specified range of enhanced florescence signal.
-
Citation: Hu J, Kan B, Liu ZH, Yu SY. Enteroaggregative
Escherichia coli isolated from Chinese diarrhea patients with high-pathogenicity island ofYersinia is involved in synthesis of siderophore yersiniabactin. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(37): 5816-5820 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i37/5816.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i37.5816