Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2005; 11(36): 5638-5643
Published online Sep 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i36.5638
Published online Sep 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i36.5638
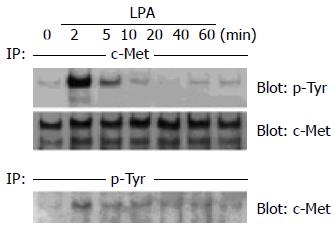
Figure 1 Rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of c-Met in response to LPA in human colon cancer cells.
(A) Human colon cancer LoVo cells were serum -starved for 24 h and then incubated with 10 µmol/L LPA for 2-60 min. After cell lysis, c -Met was immunoprecipitated (IP) using polyclonal anti-c -Met antibody, and immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with monoclonal anti-phosphotyrosine antibody. Then the membrane was stripped and immunoblotted with anti-c-Met as a control. (B) Human colon cancer LoVo cells were serum-starved for 24 h and then incubated with 10 µmol/L LPA for 2-60 min. These cell lysates were IP with anti-phosphotyrosine, and the immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with anti-c-Met.
- Citation: Shida D, Kitayama J, Yamaguchi H, Yamashita H, Mori K, Watanabe T, Nagawa H. Lysophosphatidic acid transactivates both c-Met and epidermal growth factor receptor, and induces cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human colon cancer LoVo cells. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(36): 5638-5643
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i36/5638.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i36.5638