Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2005; 11(35): 5577-5581
Published online Sep 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i35.5577
Published online Sep 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i35.5577
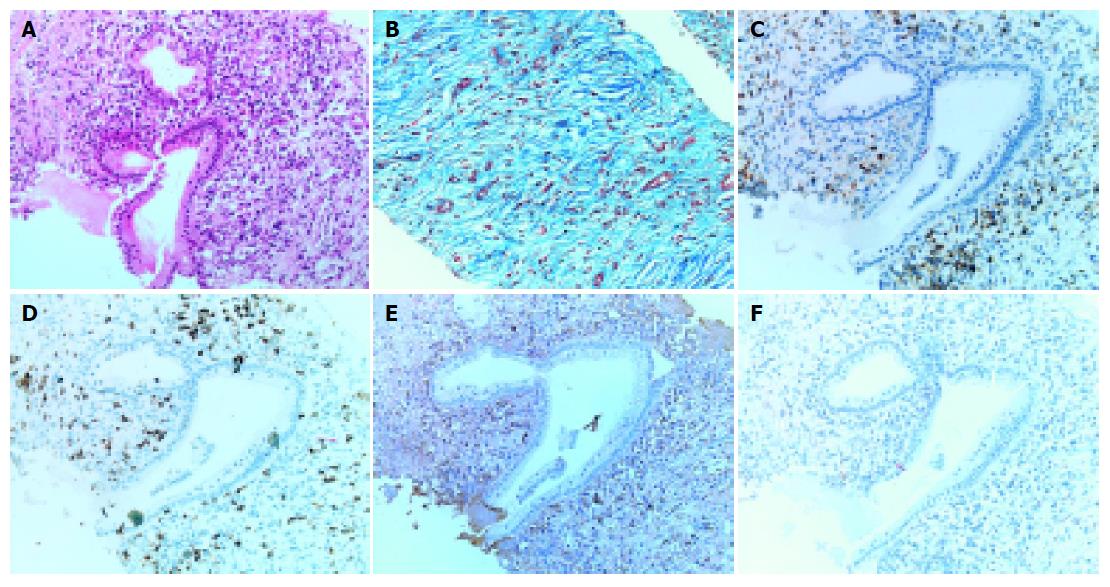
Figure 4 Histological examination of pancreatic specimen obtained by needle biopsy.
Note the extensive fibrosis, acinar atrophy, infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells were seen. The infiltrates were observed predominantly around the pancreatic duct (A: hematoxylin and eosin staining; B: Masson staining). These infiltrates consisted mainly of CD4- or CD8-positive T lymphocytes, and CD20-negative and IgG4-positive plasma cells (C-F: immunostaining of CD4, 8, IgG4, and CD20 respectively).
- Citation: Taguchi M, Aridome G, Abe S, Kume K, Tashiro M, Yamamoto M, Kihara Y, Nakamura H, Otsuki M. Autoimmune pancreatitis with IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration in salivary glands and biliary tract. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(35): 5577-5581
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i35/5577.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i35.5577