Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2005; 11(33): 5162-5168
Published online Sep 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i33.5162
Published online Sep 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i33.5162
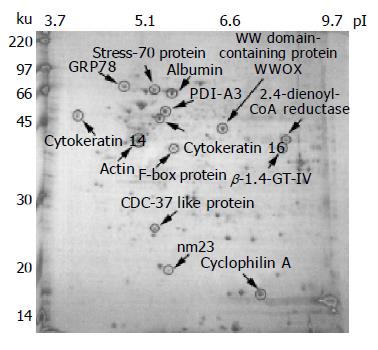
Figure 4 Proteomic analysis of the human colorectal cancer tissue lysate prepared by the MagNA Lyser.
Approximately 150 mg of tumor specimen from a colon cancer patient was subjected to tissue lysis by the new MagNA Lyser method. One aliquot (600 mg) of tissue lysate was resolved on a 13-cm IPG strip, pH 3-10, and subsequently run in a 14 cm×15 cm 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel, then visualized by staining with Coomassie blue dye. Protein spots were cut from the gel, after trypsin digestion and peptide extraction, the spots were identified through MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, and have been labeled on the gel image.
- Citation: Chen WS, Chang HY, Chang JT, Liu JM, Li CP, Chen LL, Chang HL, Chen CC, Huang TS. Novel rapid tissue lysis method to evaluate cancer proteins: Correlation between elevated Bcl-XL expression and colorectal cancer cell proliferation. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(33): 5162-5168
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i33/5162.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i33.5162