Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2005; 11(32): 4979-4985
Published online Aug 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i32.4979
Published online Aug 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i32.4979
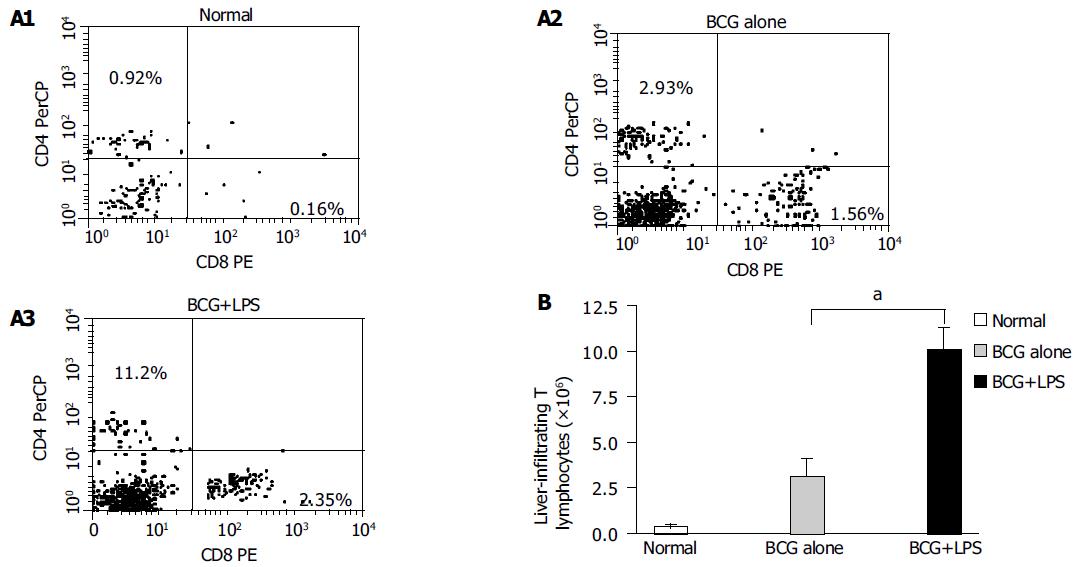
Figure 5 Analysis of liver-infiltrating CD4+ and CD8+T lymphocytes population in liver injury induced by BCG and LPS.
Mice were primed with BCG and sequentially challenged by LPS, 12 d after priming. MNCs derived from normal (without any treatment, open bars); BCG-primed (horizontal bars) and BCG-primed plus LPS challenged mice (hatched bars) were harvested for FACS analysis. A1-A3: The CD4+ and CD8+T lymphocytes population were analyzed with FACS; B: the absolute number of T lymphocytes was determined by multiplying the total MNC number by the fraction of CD4+, CD8+T-lymphocytes population. aP<0.05 vs BCG-primed mice.
- Citation: Xu HB, Gong YP, Cheng J, Chu YW, Xiong SD. CXCL16 participates in pathogenesis of immunological liver injury by regulating T lymphocyte infiltration in liver tissue. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(32): 4979-4985
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i32/4979.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i32.4979