Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2005; 11(29): 4524-4529
Published online Aug 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i29.4524
Published online Aug 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i29.4524
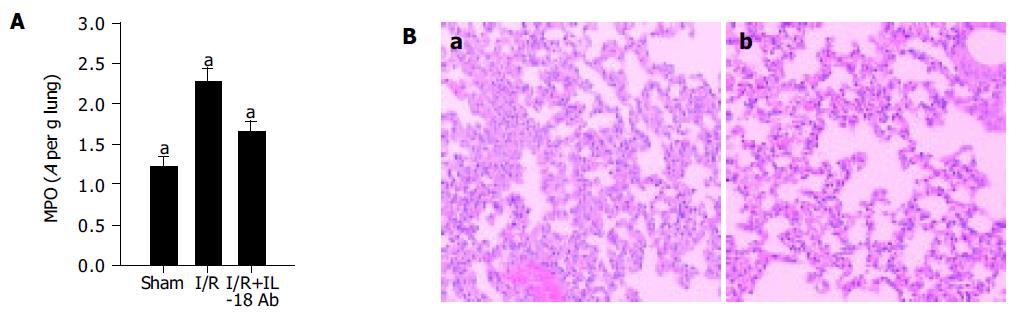
Figure 3 The effect of anti-IL-18 antibody on the ischemia-induced lung injury.
A: Anti-IL-18 antibody injection remarkably inhibited the lung MPO activity. After 3 h of reperfusion, the MPO activity was determined in lung tissues (n = 5), aP<0.05 vs others. B: Comparison of pulmonary histopathology. Lungs from ischemic mice (a, for 3 h of reperfusion), and ischemic mice treated with IL-18Ab (b, for 3 h of reperfusion) and stained with HE. Magnification ×100.
- Citation: Yang YJ, Shen Y, Chen SH, Ge XR. Role of interleukin 18 in acute lung inflammation induced by gut ischemia reperfusion. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(29): 4524-4529
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i29/4524.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i29.4524