Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2005; 11(29): 4511-4518
Published online Aug 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i29.4511
Published online Aug 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i29.4511
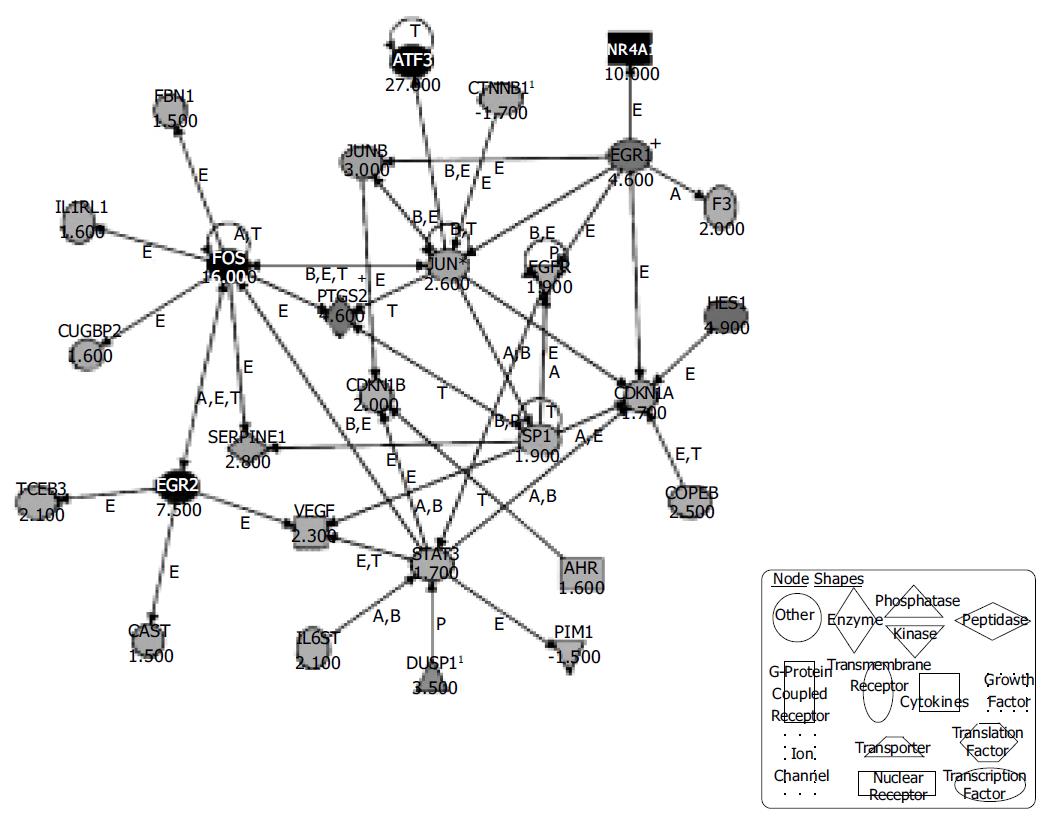
Figure 3 Ingenuity® Pathways Analysis reveals a possible network of genes activated in IEC-6 cells upon induction of the ephrin-B pathway.
Three hundred and thirty-one regulated genes with changed -P values lower than 0.003 and higher than 0.997 were selected and entered the Ingenuity® pathway analysis. The displayed network features only genes with functional interactions. Many of those genes are associated with cellular growth, proliferation and control of cell death. Arrows pointing from one gene to another indicate that one causes activation of the other one (includes any direct interaction: e.g. binding, phosphorylation, dephosphorylation, etc.). For ligands/receptors arrows pointing from a ligand to a receptor signify that the ligand binds the receptor and subsequently leads to activation of the receptor. The respective fold-changes are given below the gene symbols. Further abbreviations are: A, Activation/deactivation; B, Binding; E, Expression; M, Biochemical Modification; P, Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation; T, Transcription; 1Duplicate-user input gene that had duplicate identifiers in the dataset file mapping to a single gene in the Ingenuity® Pathways Knowledge Base. + Indicates there are other networks from the analysis that contain this gene. Gene names are: AHR: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor; ATF3: Activating transcription factor 3; CAST: Calpastatin; CDKN1A: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A; CDKN1B: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B; COPEB: Core promoter element binding protein; CTNNB1: Catenin (cadherin-associated protein), beta 1; CUGBP2: UG triplet repeat, RNA-binding protein 2; DUSP1: Dual specificity phosphatase 1; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; EGR1: Early growth response 1; EGR2: Early growth response 2; F3: Coagulation factor 3; FBN1: Fibrillin-1; FOS: v-fos FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog; HES1: Hairy and enhancer of split 1 (Drosophila); IL1RL1: Interleukin 1 receptor-like 1; IL6ST: Interleukin 6 signal transducer; JUN: v-jun sarcoma virus 17 oncogene homolog (avian); JUNB: Jun-B oncogene; NR4A1: Nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 1; PIM1: Proviral integration site 1; PTGS2: Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2; SERPINE1: Serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, member 1; SP1: Sp1 transcription factor; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TCEB3: Transcription elongation factor B (SIII), polypeptide 3; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
- Citation: Hafner C, Meyer S, Hagen I, Becker B, Roesch A, Landthaler M, Vogt T. Ephrin-B reverse signaling induces expression of wound healing associated genes in IEC-6 intestinal epithelial cells. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(29): 4511-4518
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i29/4511.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i29.4511