Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2005; 11(27): 4148-4153
Published online Jul 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i27.4148
Published online Jul 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i27.4148
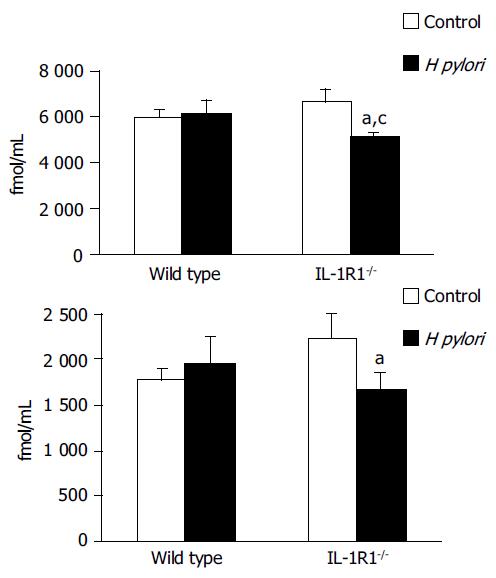
Figure 4 The gastric (A: total, B: active) ghrelin levels.
Although neither a simple lack of the IL-1 signal (spotted clear column: (A) n = 5, (B) n = 5) nor H pylori infection alone (filled column: (A) n = 5, (B) n = 5) was associated with any changes in the gastric ghrelin levels as compared with the levels in the uninfected wild-type mice (clear column: (A) n = 5, (B) n = 5), H pylori infection induced a marked decrease of the a) total and b) active gastric ghrelin levels in the IL-1R1-/-mice (spotted filled column: (A) n = 6, (B) n = 5). aP < 0.05 vs the uninfected mice; cP < 0.05 vs the wild-type mice.
-
Citation: Abiko Y, Suzuki H, Masaoka T, Nomura S, Kurabayashi K, Hosoda H, Kangawa K, Hibi T. Enhanced plasma ghrelin levels in
Helicobacter pylori -colonized, interleukin-1-receptor type 1-homozygous knockout (IL-1R1-/-) mice. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(27): 4148-4153 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i27/4148.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i27.4148