Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2005; 11(26): 4052-4060
Published online Jul 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i26.4052
Published online Jul 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i26.4052
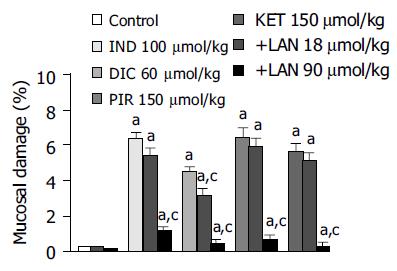
Figure 2 Histomorphometric evaluation of gastric mucosal damage in rats subjected to intragastric administration of indomethacin (IND, 100 µmol/kg), diclofenac (DIC, 60 µmol/kg), piroxicam (PIR, 150µmol/kg) or ketoprofen (KET, 150 µmol/kg) either alone or in the presence of lansoprazole (LAN, 18 and 90 µmol/kg).
Each column indicates the mean value obtained from 6-8 animals ± SE (vertical lines). aP < 0.05 vs control values; cP < 0.05 between the respective values obtained in animals treated with a test NSAID alone.
- Citation: Blandizzi C, Fornai M, Colucci R, Natale G, Lubrano V, Vassalle C, Antonioli L, Lazzeri G, Tacca MD. Lansoprazole prevents experimental gastric injury induced by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs through a reduction of mucosal oxidative damage. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(26): 4052-4060
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i26/4052.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i26.4052