Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2005; 11(26): 4024-4031
Published online Jul 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i26.4024
Published online Jul 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i26.4024
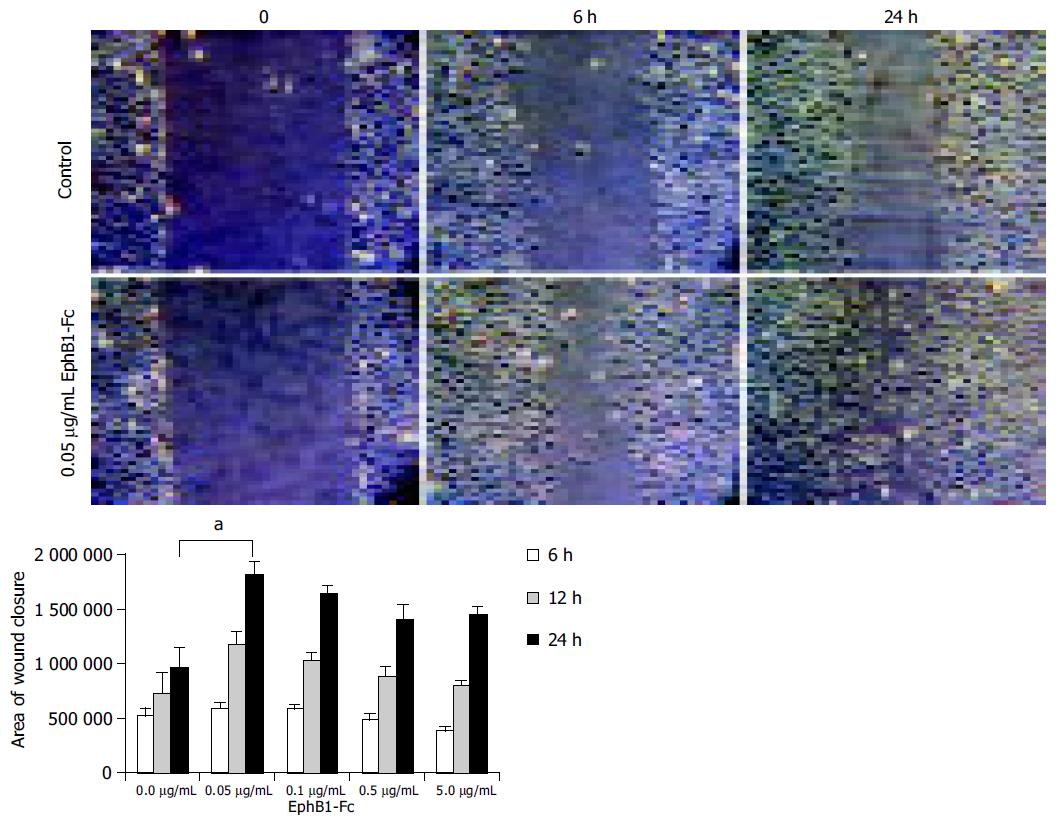
Figure 5 IEC-6 in vitro scratch wound assays indicate an enhanced wound closure activity upon stimulation with EphB1-Fc.
IEC-6 cell monolayers were wounded in a standardized manner using a cell scraper, and relative wound closure was monitored after 6 h and 24 h. Subnanomolar doses of EphB1-Fc (0.05 µg/mL~0.33 nmol/L) significantly enhanced the wound closure (aP < 0.05). Higher doses did not further increase this effect.
- Citation: Hafner C, Meyer S, Langmann T, Schmitz G, Bataille F, Hagen I, Becker B, Roesch A, Rogler G, Landthaler M, Vogt T. Ephrin-B2 is differentially expressed in the intestinal epithelium in Crohn’s disease and contributes to accelerated epithelial wound healing in vitro. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(26): 4024-4031
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i26/4024.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i26.4024