Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2005; 11(24): 3772-3777
Published online Jun 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i24.3772
Published online Jun 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i24.3772
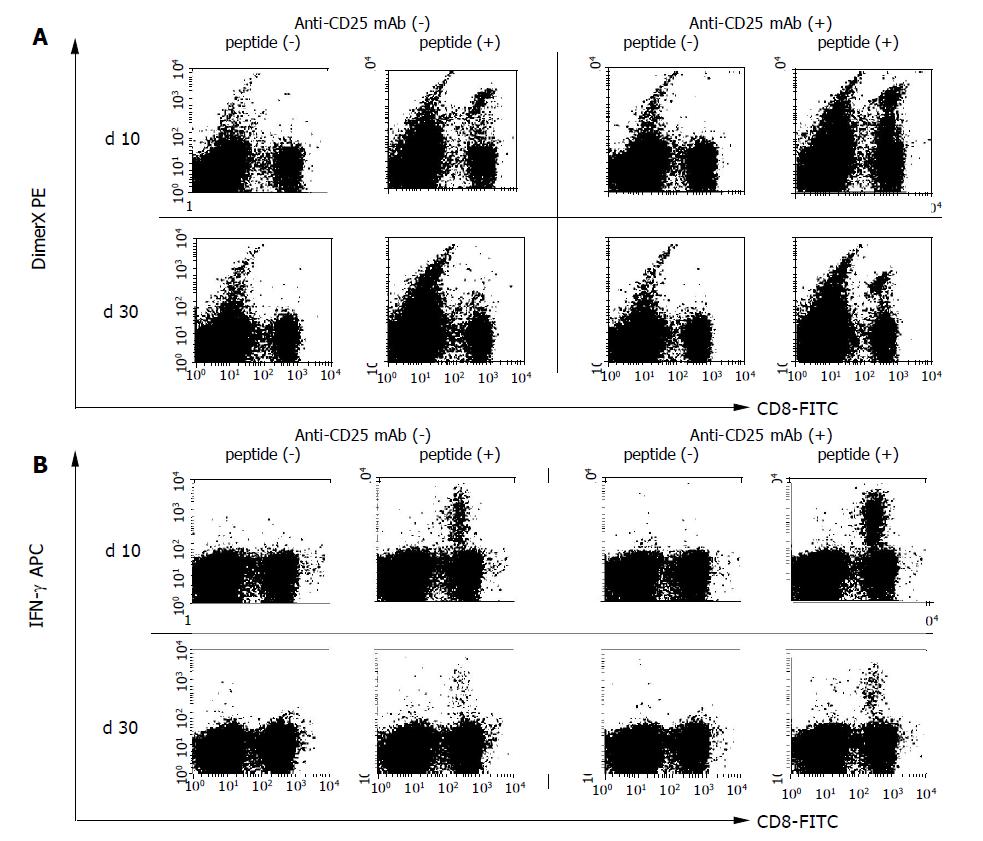
Figure 2 Flow cytometry analysis to detect HBV-specific CD8+ T cells.
Mice (six mice per group) were immunized by HBV plasmid DNA with or without anti-CD25 mAb treatment to eliminate CD25+ cells. PBMCs were harvested and the presence of HBV-specific CD8+ T cells were examined by flow cytometry on the 10 and 30 d after DNA immunization. A: HBV-specific CD8+ T cells were detected by S28-39 peptide loaded DimerX staining. Peptide unloaded empty DimerX was used as a control. B: Intracellular IFN-γ staining was performed to detect functional HBV S23-39 specific CD8+ T cells. PBMCs were incubated with 1 μg/mL of S28-39 peptide for 6 h and stained for the production of IFN-γ. Three experiments were performed with similar results. Representative responses of PBMCs from one mouse are shown in each panel.
- Citation: Furuichi Y, Tokuyama H, Ueha S, Kurachi M, Moriyasu F, Kakimi K. Depletion of CD25+CD4+T cells (Tregs) enhances the HBV-specific CD8+ T cell response primed by DNA immunization. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(24): 3772-3777
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i24/3772.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i24.3772