Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2005; 11(22): 3441-3445
Published online Jun 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i22.3441
Published online Jun 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i22.3441
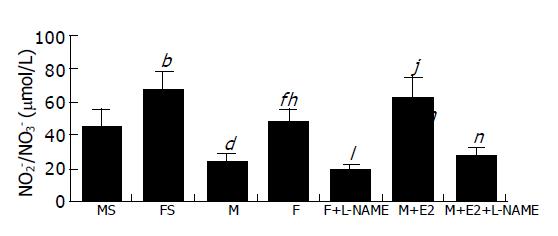
Figure 4 Serum NO2-/NO3- levels (n = 6, mean±SD).
Basal serum NO levels were significantly higher in FS group than those in MS group (bP<0.01). Although serum NO levels decreased significantly after hepatic I/R in M or F group vs MS or FS group (dP<0.01 or fP<0.01, respectively), they were still significantly higher in F group than those in M group rats (hP<0.01). When compared with male rats pretreated with saline (M group), pretreatment of male rats with E2 (M+E2 group) significantly increased serum NO levels after hepatic I/R (jP<0.01). Pretreatment with L-NAME in female rats or co-pretreatment with E2 and L-NAME in male rats significantly decreased serum NO levels vs those in F or M+E2 group rats, respectively, after hepatic I/R (lP<0.01 or nP<0.01).
- Citation: Lü P, Liu F, Wang CY, Chen DD, Yao Z, Tian Y, Zhang JH, Wu YH. Gender differences in hepatic ischemic reperfusion injury in rats are associated with endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase-derived nitric oxide. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(22): 3441-3445
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i22/3441.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i22.3441