Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2005; 11(21): 3197-3203
Published online Jun 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i21.3197
Published online Jun 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i21.3197
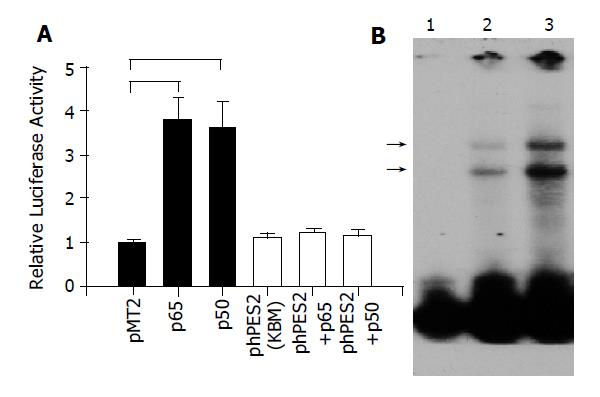
Figure 4 A: Transactivation of COX-2 promoter by NF-κB.
MKN-45 cells were transiently transfected with full-length COX-2 promoter (Black bar), or mutated COX-2 construct, phPES2 (KBM), where the putative NF-κB binding domain was mutated (open bar), in the presence of p65, p50, or control vector (pMT2) plasmid. Luciferase and β-galactosidase activities were performed 48 h after transfection. (n = 4, P<0.05); B: Binding of nuclear NF-κB to COX-2 promoter DNA in MKN-45 cells. Nuclear protein was extracted from cells cultured in the absence (lane 2), or presence (lane 3) of H pylori. The protein-DNA interaction bands were shown as (→). Lane 1 showed free probe only.
-
Citation: Wu CY, Wang CJ, Tseng CC, Chen HP, Wu MS, Lin JT, Inoue H, Chen GH.
Helicobacter pylori promote gastric cancer cells invasion through a NF-kB and COX-2-mediated pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(21): 3197-3203 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i21/3197.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i21.3197