Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2005; 11(21): 3197-3203
Published online Jun 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i21.3197
Published online Jun 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i21.3197
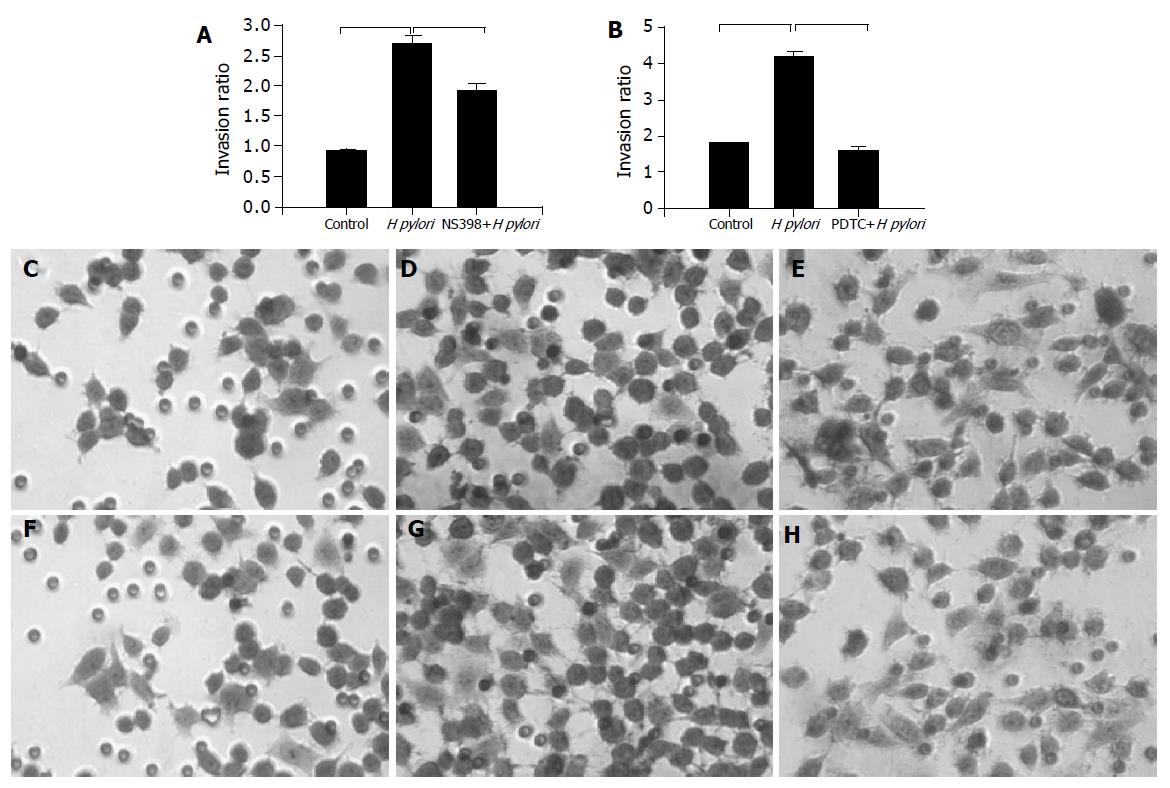
Figure 1 Effects of H pylori infection, a cox-2 (NS398), or a NF-κB inhibitor (PDTC) on gastric cancer cell invasion.
A: MKN-45 cells were treated with H pylori in the presence or absence of NS398. Cells on the lower surface of insert chamber were stained with hematoxylin for 10 min and counted under microscope with 200× magnifications. Data are presented as mean±SD of three separate experiments (P<0.05); B: MKN-45 cells were treated with H pylori in the presence or absence of PDTC (P<0.05); microscopic photos of stained migration cells: C: control; D: with H pylori; E: with H pylori and NS-398; F: control; G: with H pylori; H: with H pylori and PDTC.
-
Citation: Wu CY, Wang CJ, Tseng CC, Chen HP, Wu MS, Lin JT, Inoue H, Chen GH.
Helicobacter pylori promote gastric cancer cells invasion through a NF-kB and COX-2-mediated pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(21): 3197-3203 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i21/3197.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i21.3197