Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2005; 11(14): 2148-2153
Published online Apr 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i14.2148
Published online Apr 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i14.2148
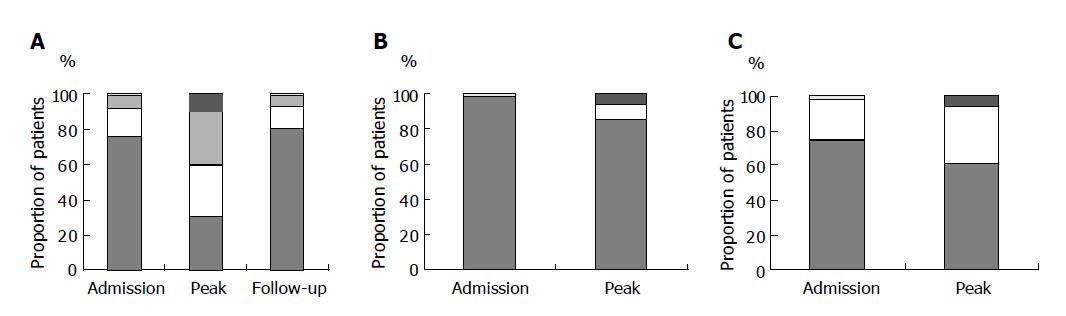
Figure 2 A: Proportion of patients with different ALT levels at initial visit (n = 294), at peak ALT (n = 293; 1 missing data) and on last follow-up (n = 264; 27 patients died, 3 missing data).
B: Proportion of patients with different serum bilirubin levels at initial visit (n = 294) and at peak bilirubin (n = 293, 1 missing data). C: Proportion of patients with different prothrombin time at initial visit (n = 293, one missing data) and at peak prothrombin time (n = 283, 11 missing data).
- Citation: Chan HLY, Kwan ACP, To KF, Lai ST, Chan PKS, Leung WK, Lee N, Wu A, Sung JJY. Clinical significance of hepatic derangement in severe acute respiratory syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(14): 2148-2153
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i14/2148.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i14.2148