Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2005; 11(14): 2101-2108
Published online Apr 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i14.2101
Published online Apr 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i14.2101
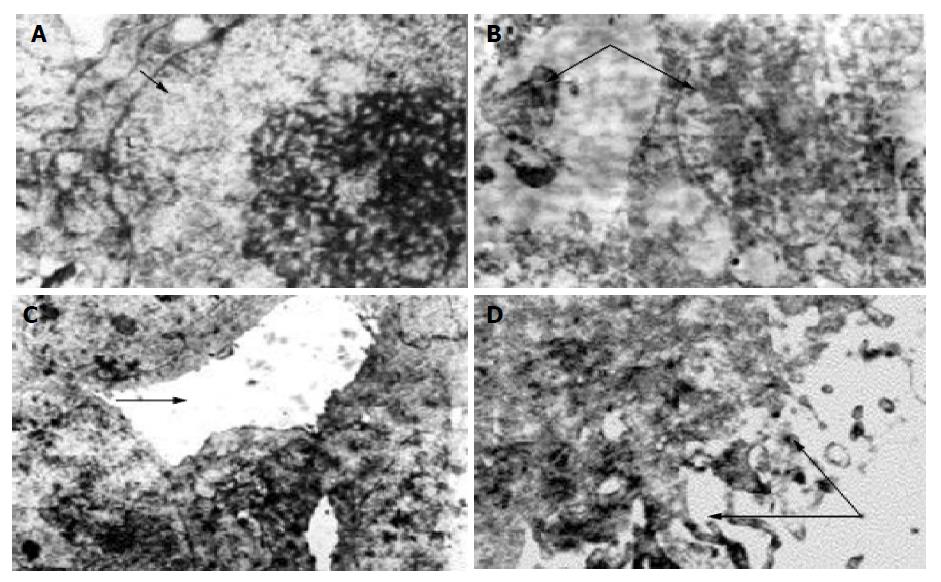
Figure 3 TEM shows the changes in Pc-3 tumor cell; A: Tumor cells (arrow) in control group grew vividly with large nuclei and some nucleoli (12×103×1.
2); B: Tumor cells (arrow) were damaged, only the contour of nucleus remained (6×103); C: A few remaining tumor cells arranged as a glandular lumen (arrow) with small nucleoli (8×103×1.2); D: At low dose point, well differentiated Pc-3 cell with small nucleoli, plenty of euchromatin, many long micro-villi on cell surface (arrow), glandular lumens interplaced between the cells having the tendency of exocrine formation (15×103×1.2).
- Citation: Liu L, Feng GS, Gao H, Tong GS, Wang Y, Gao W, Huang Y, Li C. Chromic-P32 phosphate treatment of implanted pancreatic carcinoma: Mechanism involved. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(14): 2101-2108
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i14/2101.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i14.2101