Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2005; 11(10): 1426-1432
Published online Mar 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i10.1426
Published online Mar 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i10.1426
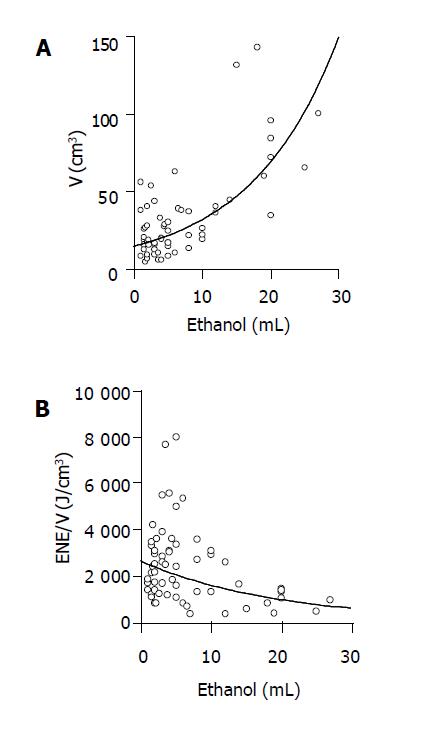
Figure 2 Relationship between the amount of ethanol injected and the volume of coagulated necrosis or the energy requirement for inducing per unit volume of coagulated necrosis in PEI-RFA.
PEI-RFA was performed on 60 patients with HCC. The ablation was done by using the Cool-tip RF system. The amount of ethanol injected into tumors positively correlated with the volume of coagulated necrosis (A: r = 0.71, P<0.0001) and it negatively correlated with the energy requirement for inducing per unit volume of coagulated necrosis (B: r = -0.41, 0.014).
- Citation: Kurokohchi K, Watanabe S, Masaki T, Hosomi N, Miyauchi Y, Himoto T, Kimura Y, Nakai S, Deguchi A, Yoneyama H, Yoshida S, Kuriyama S. Comparison between combination therapy of percutaneous ethanol injection and radiofrequency ablation and radiofrequency ablation alone for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(10): 1426-1432
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i10/1426.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i10.1426