Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2005; 11(10): 1420-1425
Published online Mar 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i10.1420
Published online Mar 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i10.1420
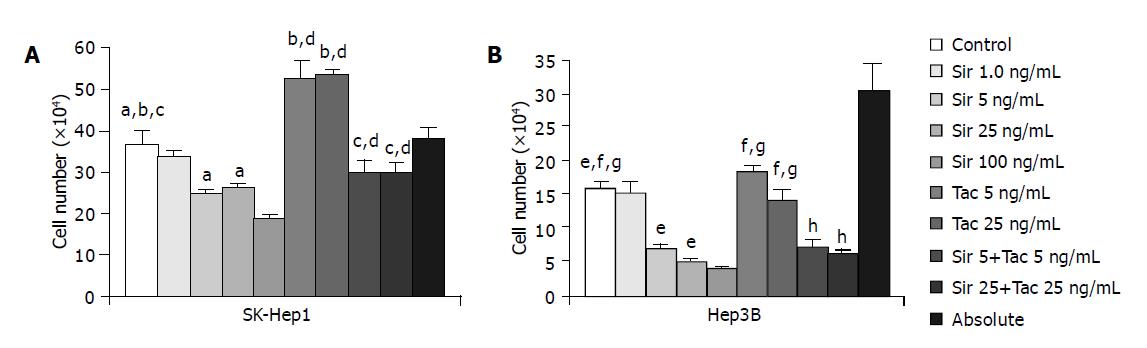
Figure 1 Proliferation assays showing cell numbers from mean counts of three experiments.
Cells were treated as described in Materials and Methods with sirolimus, tacrolimus, or the combination of both. Sir = sirolimus; Tac = tacrolimus. Data are expressed as mean±SE. (A: SK-Hep 1: aP = 0.0105; bP = 0.0156; cP = 0.254; dP<0.0001; B: Hep 3B: eP<0.0001; fP = 0.0654; gP = 0.0002; hP<0.0001).
- Citation: Schumacher G, Oidtmann M, Rueggeberg A, Jacob D, Jonas S, Langrehr JM, Neuhaus R, Bahra M, Neuhaus P. Sirolimus inhibits growth of human hepatoma cells alone or combined with tacrolimus, while tacrolimus promotes cell growth. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(10): 1420-1425
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i10/1420.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i10.1420