Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2005; 11(1): 142-148
Published online Jan 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i1.142
Published online Jan 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i1.142
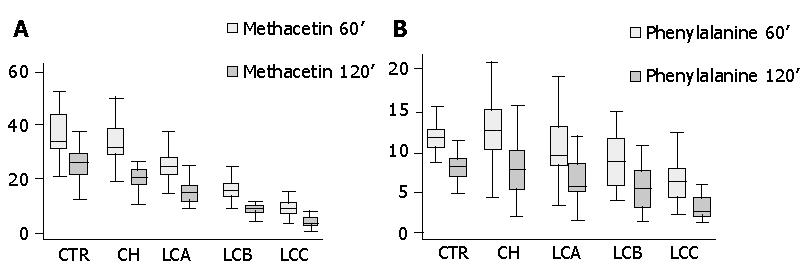
Figure 1 Methacetin and phenylalanine breath tests: cumulative percent of oxidation at 60 and 120 min.
A: Methacetin breath test: cumulative percent of oxidation at 60 and 120 min. CTR = controls; CH = chronic hepatitis; LCA = liver cirrhosis Child A; LCB = liver cirrhosis Child B; LCC = liver cirrhosis Child C. CTR vs CH, LCA, LCB, LCC: P<0.001 CH vs LCA, LCB, LCC: P<0.001 LCA vs LCB, LCC: P<0.001 LCB vs LCC: P<0.001. B: Phenylalanine breath test: cumulative percent oxidation at 60 and 120 min. CTR = controls; CH = chronic hepatitis; LCA = liver cirrhosis Child A; LCB = liver cirrhosis Child B; LCC = liver cirrhosis Child C. CTR vs LCB, LCC: P<0.001 CH vs LCB, LCC: P<0.001 LCA vs LCC: P<0.05.
- Citation: Festi D, Capodicasa S, Sandri L, Colaiocco-Ferrante L, Staniscia T, Vitacolonna E, Vestito A, Simoni P, Mazzella G, Portincasa P, Roda E, Colecchia A. Measurement of hepatic functional mass by means of 13C-methacetin and 13C-phenylalanine breath tests in chronic liver disease: Comparison with Child-Pugh score and serum bile acid levels. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(1): 142-148
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i1/142.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i1.142