Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 15, 2004; 10(8): 1082-1087
Published online Apr 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i8.1082
Published online Apr 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i8.1082
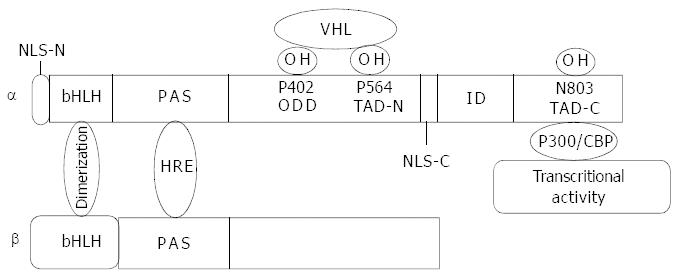
Figure 1 Molecular structure of HIF-1α and HIF-1β.
bHLH domain mediates dimerization of the two subunits. PAS domain is responsible for DNA binding. Proline residues of 402 and 564 at ODD domain are hydroxylized by proline hydroxylase and recog-nized by VHL and then targeted to the ubiquitin proteasome pathway. Asn803 at the C-terminal transactivation domain (TAD-C) is hydroxylized by FIH-1 (factor inhibiting HIF-1) with a result of inhibition of HIF-1α interaction with co-activator p300 and conse-quently inhibits transcriptional activity. The nuclear location signal at C-terminal functions in HIF-1α translocation into nuclei.
- Citation: Shi YH, Fang WG. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in tumour angiogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(8): 1082-1087
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i8/1082.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i8.1082