Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 15, 2004; 10(6): 875-880
Published online Mar 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i6.875
Published online Mar 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i6.875
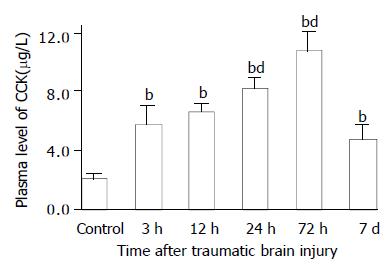
Figure 3 Alteration of CCK in plasma after TBI.
Compared with control, plasma level of CCK was significantly increased postinjury, and peaked at 72 h, then declined to some degree on d 7, but was still significantly higher than that of control. bP < 0.01 vs control; dP < 0.01 vs 3 h. Mean ± SD of 6 animals, control: 2.1 ± 0.3 µg/L, 3 h: 5.8 ± 1.2 µg/L, 12 h: 6.7 ± 0.5 µg/L, 24 h: 8.3 ± 0.7 µg/L, 72 h: 10.8 ± 1.2 µg/L, 7 d: 4.8 ± 0.9 µg/L.
- Citation: Hang CH, Shi JX, Li JS, Wu W, Li WQ, Yin HX. Levels of vasoactive intestinal peptide, cholecystokinin and calcitonin gene-related peptide in plasma and jejunum of rats following traumatic brain injury and underlying significance in gastrointestinal dysfunction. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(6): 875-880
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i6/875.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i6.875