Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 15, 2004; 10(24): 3590-3596
Published online Dec 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i24.3590
Published online Dec 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i24.3590
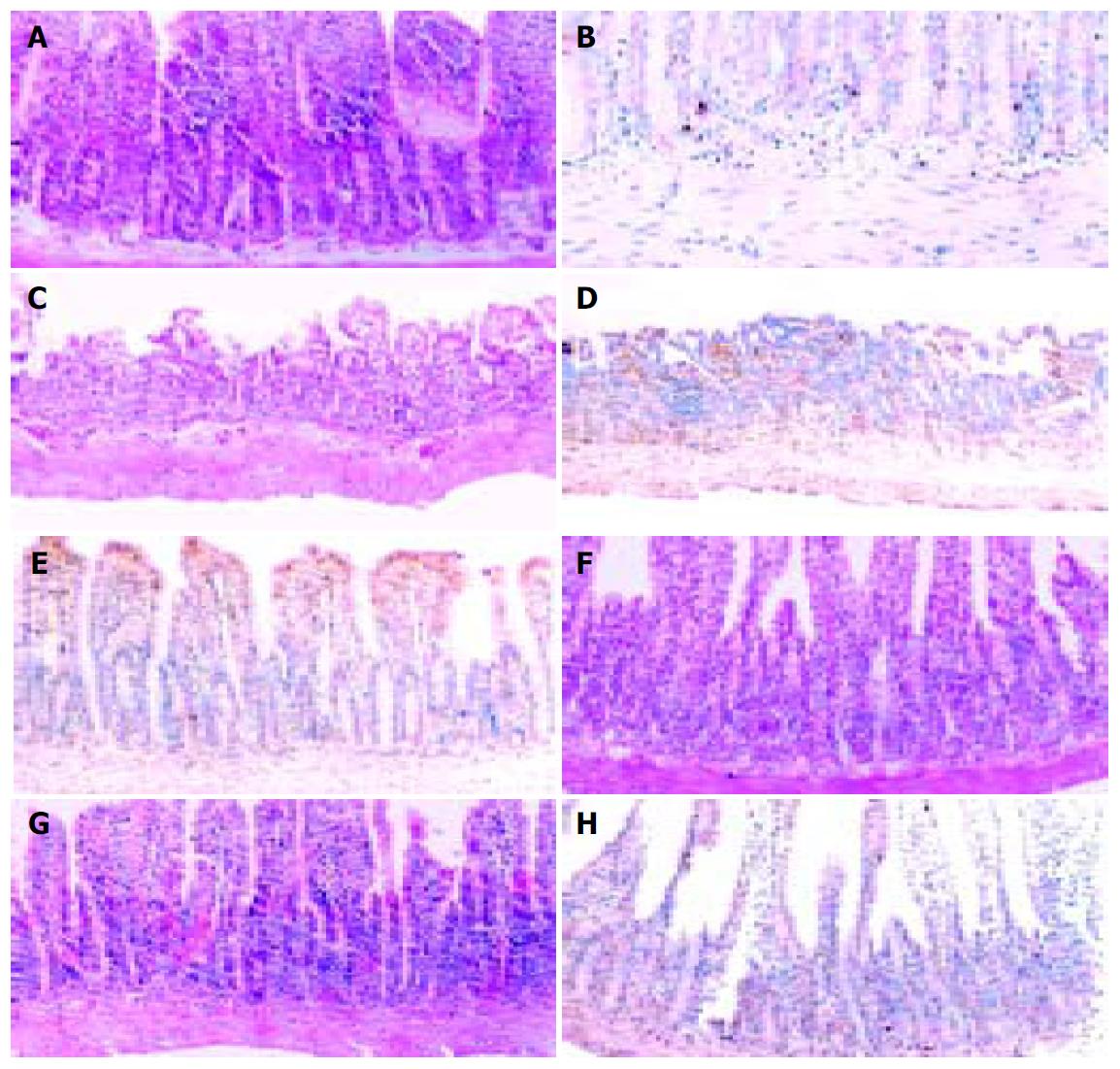
Figure 4 Morphological examination and immunohistochemical detection and quantification of apoptosis based on the label-ling of DNA strand breaks (Roche Applied Science, Germany).
A: Marked epithelial separation from the basement, subepithelial edema, haemorrhage, erosion. C: Necrosis in I/R plus saline control group. E and G: Tissue damage reduction in both aFGF and aFGF28-154 treated groups. B: Immunohistochemical detection and quantification of apoptosis in normal epithelium entericum. D: Increased number of apoptotic cells in epithelium entericum in rats treated with saline. F and H: Significant reduction of apoptotic cells in epithelium entericum in rats treated with both aFGF and aFGF28-154.
- Citation: Fu XB, Li XK, Wang T, Cheng B, Sheng ZY. Enhanced anti-apoptosis and gut epithelium protection function of acidic fibroblast growth factor after cancelling of its mitogenic activity. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(24): 3590-3596
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i24/3590.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i24.3590