Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 15, 2004; 10(22): 3318-3321
Published online Nov 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i22.3318
Published online Nov 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i22.3318
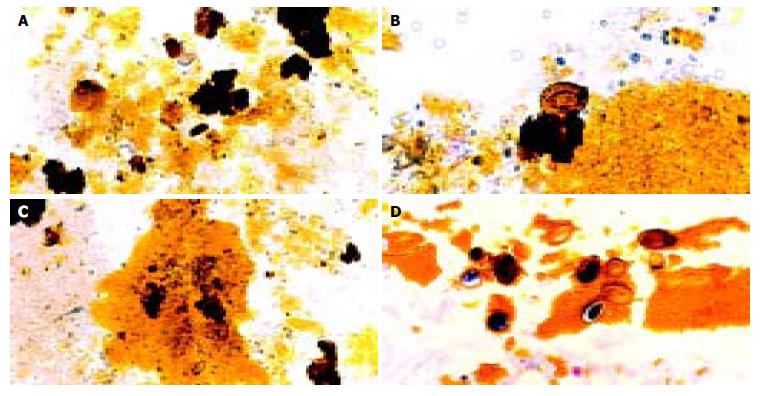
Figure 2 Typical pictures showing the cascades of Opisthorchis egg-associated stone formation starting from aggregation of the eggs admixed with mucin (A), deposition of calcium bilirubinate on the eggshells (B), and formation of tiny stones (C & D).
Original magnification, × 100 (A & C) and × 200 (B & D).
- Citation: Sripa B, Kanla P, Sinawat P, Haswell-Elkins MR. Opisthorchiasis-associated biliary stones: Light and scanning electron microscopic study. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(22): 3318-3321
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i22/3318.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i22.3318