Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 15, 2004; 10(2): 205-208
Published online Jan 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i2.205
Published online Jan 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i2.205
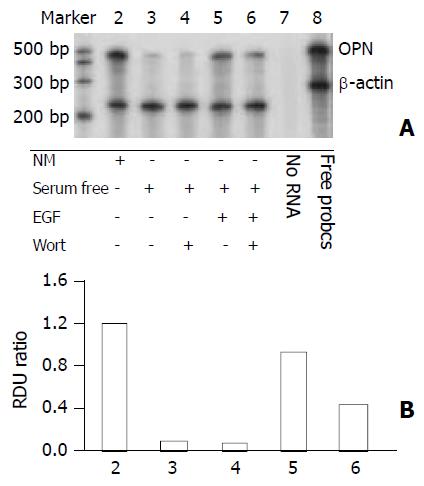
Figure 3 Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway dependent of osteopontin expression in HepG2 cells.
The PI3-kinase in-hibitor wortmannin was used to assess EGF-dependent sig-nal transduction leading to osteopontin gene expression. 1×105 cells were plated in 6-well plates. Next morning, cell cultures (near 80% confluent) were incubated in serum-free medium for 24 hours. 100 nM wortmannin was added to the cells 30 minutes before incubation in the presence or absence of 10 ng/ml EGF. A. Osteopontin mRNA level was analyzed by RNase protection assay on total RNA using a 486 base-pair probe and controlling the loading with a probe for β-actin. B. Quantitation of osteopontin mRNA levels is shown in (A). RDU ratio reflects relative density units of osteopontin mRNA divided by β-actin mRNA.
- Citation: Zhang GX, Zhao ZQ, Wang HD, Hao B. Enhancement of osteopontin expression in HepG2 cells by epidermal growth factor via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(2): 205-208
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i2/205.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i2.205