Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 15, 2004; 10(2): 155-160
Published online Jan 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i2.155
Published online Jan 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i2.155
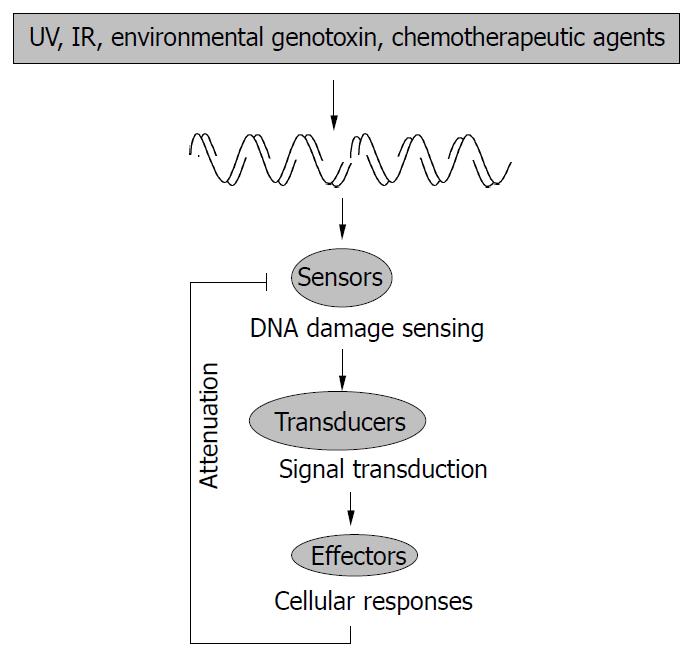
Figure 1 A general schematic representation of cellular re-sponses to genotoxic stress.
Ultraviolet (UV), ionizing radia-tion (IR), and various chemicals can induce DNA damage, such as double strand breaks (DSBs), which can be detected by “sensors”. This generates some signal that can be transduced by the transducers to effector molecules. Finally, there is the presence of an attenuation mechanism to control the cellular response to genotoxic stress.
- Citation: Yang J, Xu ZP, Huang Y, Hamrick HE, Duerksen-Hughes PJ, Yu YN. ATM and ATR: Sensing DNA damage. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(2): 155-160
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i2/155.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i2.155