Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 1, 2004; 10(17): 2524-2528
Published online Sep 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i17.2524
Published online Sep 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i17.2524
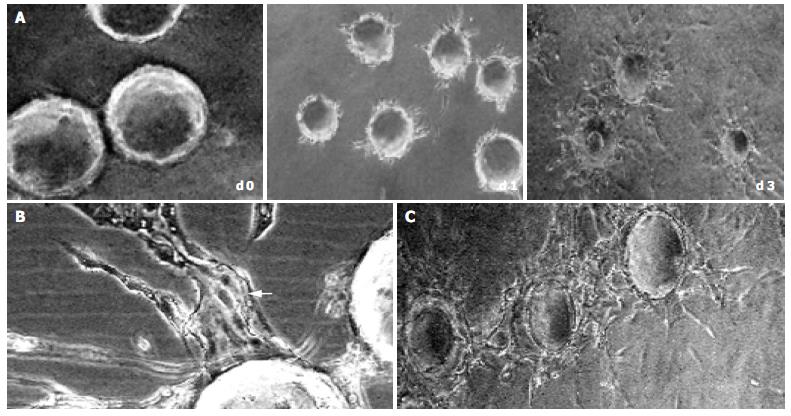
Figure 2 Sequential steps of capillary formation.
During 3 d after polymerization of the fibrin gel, the HMVECs (bFGF 40 ng/mL) on microcarriers migrated into fibrin matrix to form sprouts, which elongated (A) with intracellular or intercellular lumina formed (bFGF 40 ng/mL). The lumina frequently contained cellular debris, which can be seen to float by shaking the culture dishes, indicating that lumina contents had liquefied (B, arrow). In the late stage (d 5), the capillary sprouts anastomosed to each other, and finally formed capillary-like network (C) (original magnification × 100).
-
Citation: Sun XT, Ding YT, Yan XG, Wu LY, Li Q, Cheng N, Qiu YD, Zhang MY. Angiogenic synergistic effect of basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor in an
in vitro quantitative microcarrier-based three-dimensional fibrin angiogenesis system. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(17): 2524-2528 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i17/2524.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i17.2524