Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 1, 2004; 10(13): 1902-1906
Published online Jul 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1902
Published online Jul 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1902
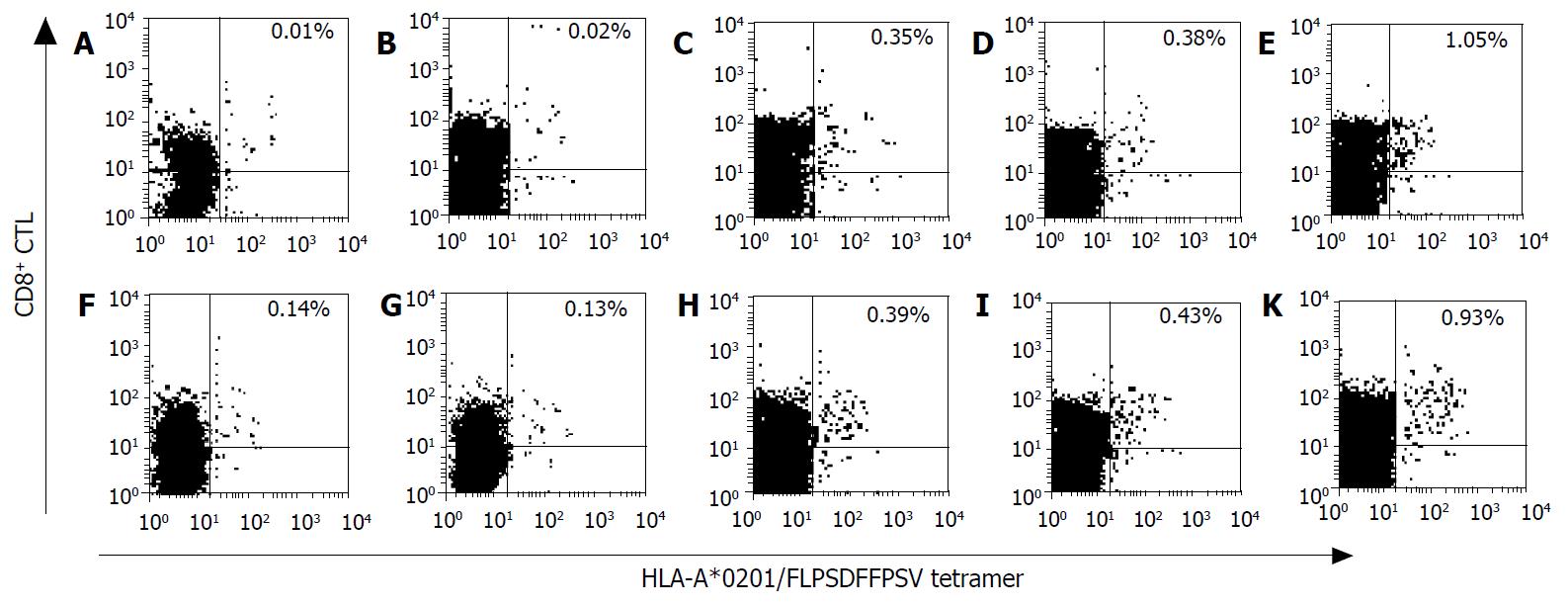
Figure 1 Detection of the HBcAg18-27-specific CD8+ T cells produced with HLA-A*0201/FLPSDFFPSV tetramer-binding assay.
A: Non-stimulated HLA-A2+ PBMCs from healthy donors; B: Irrelevant peptide pulsed HLA-A2+ PBMCs from healthy donors; C: Peptide1 pulsed HLA-A2+ PBMCs from healthy donors; D: Peptide2 pulsed HLA-A2+ PBMCs from healthy donors; E: Peptide3 pulsed HLA-A2+ PBMCs from healthy donors; F: Non-stimulated HLA-A2+ PBMCs from chronic hepatitis patients; G: Irrelevant peptide pulsed HLA-A2+ PBMCs from chronic hepatitis patients; H: Peptide1 pulsed HLA-A2+ PBMCs from chronic hepatitis patients; I: Peptide2 pulsed HLA-A2+ PBMCs from chronic hepatitis patients; K: Peptide3 pulsed HLA-A2+ PBMCs from chronic hepatitis patients.
- Citation: Shi TD, Wu YZ, Jia ZC, Zou LY, Zhou W. Therapeutic polypeptides based on HBV core 18-27 epitope can induce CD8+ CTL-mediated cytotoxicity in HLA-A2+ human PBMCs. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(13): 1902-1906
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i13/1902.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1902