Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 15, 2003; 9(11): 2539-2543
Published online Nov 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i11.2539
Published online Nov 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i11.2539
Figure 1 Pretreated bile centrifuged at 45000 rev/min and divided into three fractions.
Horizontal arrows indicate the vesicular phase bile.
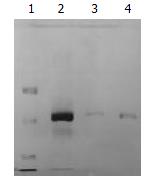
Figure 2 Purified 33.
5 kDa vesicular proteins from three different bile samples run on SDS-PAGE. Lane 1: protein marker, Lanes 2-4: the 33.5 kDa vesicular protein.
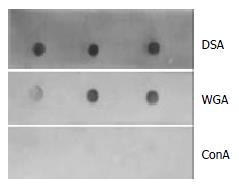
Figure 3 Lectin affinity staining with DSA, WGA, Con A labeled with peroxidase.
The 33.5 kDa vesicular protein was strongly connected with DSA, and weakly bound to WGA, but did not react with Con A.
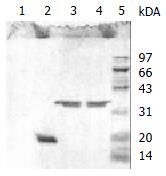
Figure 4 SDS-PAGE (reduced condition) of the 33.
5 kDa vesicular protein after N-deglycosylation, O-deglycosylation and proteolysis. Complete disappearance was observed after incubation with Pronase K at lane 1. A single 21 kDa band was stained after treated with N-glycanase at lane 2, but no change of the protein after enzymatic O-deglycosylation at lane 3. The band of lane 4 and lane 5 represented the 33.5 kDa vesicular protein and protein marker respectively.
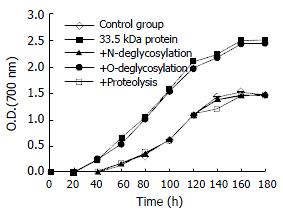
Figure 5 Promoting effect of 33.
5 kDa vesicular protein and its enzymatic products on cholesterol crystal growth curves in model bile (TL = 125 g/L, BA/PL = 4.4, CSI = 1.4). All curves are given as the mean ± SD, n = 4. P < 0.05 vs control at each time.
- Citation: Xiang JB, Cai D, Ma BJ, Cha XL, Wang LY, Mo HQ, Zhang YL. Purification and characterization of 33.5 kDa vesicular protein in human bile. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(11): 2539-2543
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i11/2539.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i11.2539